These are some scripts to convert various features and annotations into a GFF-like file for use in genome browsers. There are also general purpose tools for genome annotation.
GFF (generic feature format) is a tab-delimited pseudoformat for annotating genomes, consisting of 8 well-defined columns, and a free-text 9th column (with some "guidelines" of what to include). Most work in fixing a GFF involves fixing the final column. While this is not a great format, most formats are insufficient for one reason or another. Ultimately, it would be better if certain fields were explicit, like ID (a unique machine-understandable identifier, which could be accession, etc.), Parent (any other ID), and Name (like gene name). This would also allow for fast indexing or sorting by ID, Parent, or Name, which would also make it easier to extract or process genes or features for graphics.
| Column | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | seqid | The sequence ID, usually this is the contig, scaffold or chromosome (e.g. ctg0123, scaffold_99, chrX), and NOT the name of the gene or feature (which goes in column 9) |
| 2 | source | Usually the program that generated the data (e.g. blastp, AUGUSTUS) |
| 3 | type | Type of feature (e.g. gene, exon), typically using standarized terms |
| 4 | start | First base in the feature |
| 5 | end | Last base the feature |
| 6 | score | Float (of an arbitrary scale), could be something like coverage (say 0-1000), percent identity (0.0-100.0) |
| 7 | strand | Which DNA strand, as forward (+), reverse (-), unstranded (.) or unknown (?) |
| 8 | phase | Phase of the coding sequence as 0, 1, or 2 (i.e. whether the exon ends mid-codon), only applies to CDS features |
| 9 | attributes | All other information, as a string of pairs of key=value;, though this is variable depending on version or program. Most problems with GFF are problems with parsing information from this column. |
Many of these tools were used in our analysis of the genome of the sponge Tethya wilhelma. Please cite the paper: Mills, DB. et al (2018) The last common ancestor of animals lacked the HIF pathway and respired in low-oxygen environments. eLife 7:e31176.
- pfam2gff.py PFAM domains of proteins/coding sequences made into a GFF
- blast2gff.py blast hits directly on a genome (i.e. the scaffolds) to GFF, generally indicating exons or conserved domains
- blast2genomegff.py make features of blast hits against transcripts, showing the span of target proteins and include the splicing
- microsynteny.py using two GFF files of two different genomes and blast hits, determine blocks of conserved gene order
- extract_coordinates.py extract gene or exon information to draw diagrams that look like a genome browser
By convention, the longest chromosomes are numbered first. This naturally applies to scaffolds as well. Contigs/scaffolds can be renumbered and reordered with number_contigs_by_length.py script. Use the option -c to specify an additional output file of the conversion vector, that can be used to rename the scaffold column in any GFF file with the rename_gtf_contigs.py script.
This has two modes: one will convert the "tabular" hmmscan output (generated using PFAM-A database (Pfam-A.hmm), which can be found in the FTP section of PFAM as the hmm database) into a protein GFF with domains at the protein positions. The other mode will generate a genome-GFF with the domain positions mapped onto the protein features, i.e. that the domains will fit into/across exons.
hmmscan --domE 0.1 --cpu 4 --domtblout stringtie.pfam.tab ~/PfamScan/data/Pfam-A.hmm stringtie_transdecoder_prots.fasta > stringtie.pfam.log
pfam2gff.py -i stringtie.pfam.tab > stringtie.pfam.gff
The other output will convert the domain positions into genomic coordinates for use in genome browsers, so individual domains can be viewed spanning exons. Run hmmscan as above, then use the -g option to include genomic coordinates. Use -T for presets for TransDecoder genome GFF file.
pfam2gff.py -g stringtie_transdecoder.gff -i stringtie.pfam.tab -T > stringtie_transdecoder_pfam_domains.gff
For AUGUSTUS proteins (using extract_features.py or translated nucleotides), this would be run as:
hmmscan --domE 0.1 --cpu 4 --domtblout renilla_test_prots.pfam.tab ~/db/Pfam-A.hmm renilla_test_prots.fasta > /dev/null
Then run with the AUGUSTUS GFF (ensure this is GFF format and not GTF), instructing to use CDS features as exons with -x. Depending on version, the AUGUSTUS output might appear as below, where ID is not explicitly given in the attributes of the gene or transcripts (it just says g1), but is given for the introns or CDS. This makes it difficult to parse in a standarized way.
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS gene 921 9763 0.03 + . g1
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS transcript 921 9763 0.03 + . g1.t1
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS intron 1118 2513 0.83 + . transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1";
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS CDS 921 1117 0.57 + 0 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1";
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS CDS 2514 2647 1 + 1 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1";
This should be changed to appear as GFF format. Introns are ignored anyway (thus can be removed) and CDS features will be treated as exons (with option -x).
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS gene 921 9763 0.03 + . ID=g1;Name=g1
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS mRNA 921 9763 0.03 + . ID=g1.t1;Parent=g1;Name=g1.t1
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS CDS 921 1117 0.57 + 0 Parent=g1.t1
jcf7180000021585 AUGUSTUS CDS 2514 2647 1 + 1 Parent=g1.t1
This can be run with pfam2gff.py, specifying the GFF file with -g (this will also make it print a GFF of genomic coordinates).
pfam2gff.py -g aug_nocomments_cds.gff -e 1e-3 -i aug_prots.pfam.tab -x > aug_prots_pfam.gff
Produces the following example output. The results are not filtered by position, so it is evident that 3 different von Willebrand domains are found, though group 1 is clearly the strongest match, as indicated by the score column.
jcf7180000021585 hmmscan PFAM 1011 1117 113.3 + . ID=g1.t1.VWA.1;Name=PF00092.VWA.von_Willebrand_factor_type_A_domain
jcf7180000021585 hmmscan PFAM 2514 2585 113.3 + . ID=g1.t1.VWA.1;Name=PF00092.VWA.von_Willebrand_factor_type_A_domain
jcf7180000021585 hmmscan PFAM 1014 1117 55.5 + . ID=g1.t1.VWA_2.1;Name=PF13519.VWA_2.von_Willebrand_factor_type_A_domain
jcf7180000021585 hmmscan PFAM 2514 2526 55.5 + . ID=g1.t1.VWA_2.1;Name=PF13519.VWA_2.von_Willebrand_factor_type_A_domain
jcf7180000021585 hmmscan PFAM 1011 1117 35.1 + . ID=g1.t1.VWA_3.1;Name=PF13768.VWA_3.von_Willebrand_factor_type_A_domain
jcf7180000021585 hmmscan PFAM 2514 2566 35.1 + . ID=g1.t1.VWA_3.1;Name=PF13768.VWA_3.von_Willebrand_factor_type_A_domain
Convert a PFAM protein GFF (above) to the PFAM clans, and remove some redundant hits, essentially just changing the names of the domains and merging duplicates. This is needed for the pfampipeline.py script. This script requires the clan links file, called Pfam-A.clans.tsv.
BioPython is required for this step, to get the length of each sequence.
Requires BioPython, HMMER, PFAM-A and SignalP
Script to generate graph of domains for a FASTA file of proteins. Both of the above scripts (pfam2gff.py and pfamgff2clans.py) are automatically called, followed by SignalP and the R script draw_protein_gtf.R. This is called as a command on a protein file, for example on the test dataset of nidogen proteins. The graph below illustrates some of the difficulty in identifying true orthologs, as the domain structure is quite variable between phyla.
pfampipeline.py test_data/nidogen_full_prots.fasta
Several output files are automatically generated, including the domain assignments in a GFF-like format, and a PDF of the domains, where a black line indicates the protein length, black box is the signal peptide, and colors correspond to different domains. Note that some domains may overlap, due to bad calls in the HMM. Domains are by definition non-overlapping, thus these must be removed. Automatic removal may be implemented in the future.
To view exon structure from a GFF file on a 3D protein structure, see instructions at my PDBcolor repo. Below is an example using human nidogen1, with the structure from Alphafold2:
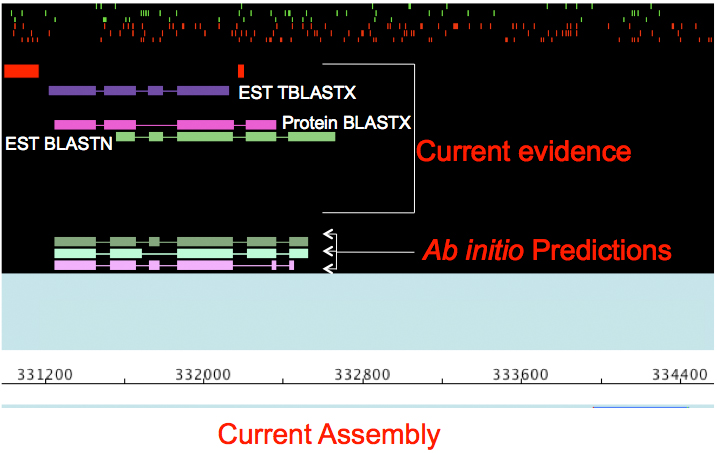
This was a strategy to convert blast hits into gene models. The direction of the blast hit and the grouping of blast hits in the same region is most indicative of a gene (though possibly pseudogenes as well). In general, blasting all human proteins against the target genome can find many proteins even in distantly related organisms. Repeated domains or very common domains (like ATP binding for kinases) will show up all over the place, so limiting the -max_target_seqs is advisable.
- Blast a protein set against the genome, and make use of the multithreading power of blast.
tblastn -query proteins.fa -db target_genome.fa -num_threads 16 -outfmt 6 > prots_vs_genome.tab
- Run blast2gff.py on the output file. This will reformat the tabular blast hits into gff3 alignment style. Simple filtering options can be applied with
-e-sand-F. If the queries were from SwissProt, use the-Soption to correctly format the SwissProt fasta headers for the output.
blast2gff.py -b prots_vs_genome.tab > prots_vs_genome.gff3
As above for the domains in pfam2gff.py, entire blast hits to transcripts or proteins can be printed as GFF using the blast2genomegff.py script, where the blast hits will be shown spanning multiple exons as a single feature. This might help to identify erroneously fused genes. Using transcripts from a de novo transcriptome Trinity, or genome guided StringTie, convert blastx protein matches into genomic coordinates. For Trinity transcripts, the coordinates on the genome need to be determined by mapping the transcripts to the genome. This can be done with GMAP. Generically, this would be run as:
blastx -query transcripts.fasta -db uniprot_sprot.fasta -num_threads 16 -outfmt 6 -max_target_seqs 5 > transcripts_sprot.tab
blast2genomegff.py -b transcripts_sprot.tab -d uniprot_sprot.fasta -g transcripts.gtf > transcripts_sprot.genome.gff
-p: program, by default isblastx, but change toblastpif proteins were used. The correct blast program is needed to calculate the intervals correctly, as blastp results need to be converted to nucleotide coordinates.-x: if starting from proteins, and theCDSfeatures are available (such as fromAUGUSTUS), use CDS features from the GFF instead of exons (that is, exons are not specified at all). If exons are specified as well and are mostly identical to CDS, then also use the option--skip-exons.-D: delimiter for spliting names in the tabular blast output. For example, if names weregene1.CDS, the option-D .would be used to split atgene1.-F: as above for-D, but to split the IDs in the GFF. If the query column in blast (first column) and the ID in the GFF do not match, and there is no output, then this or-Dmay fix the problem.-c: coverage cutoff, remove queries where the hit is under 0.1 of the subject length-e: E-value cutoff, by default is 1e-3-s: bitscore/length cutoff, remove hits with bitscore/length of under 0.1, that is, remove very distant matches. Set higher for more closely related species (0.3) or lower for distance species (0.05).-G: ignoregenefeatures, or other high-level features likemRNAortranscript, and instead extract the ID directly from each exon. This might be more convenient to use if exons are given unique IDs in the GFF, likegene1.t1.exon1. This is typically used with-F, as-G -F "."-S: specifies that the target proteins are from SwissProt/UniProt. This is required for using--add-accession, and usually for--add-description, though the description should work anyway, but will not be parsed correctly.
StringTie transcripts can be converted to fasta using the script cufflinks_gtf_genome_to_cdna_fasta.pl (packaged with TransDecoder). These are used as input for blastx. Note that with blastx, some can hit antisense, which suggests there is a protein on the antisense strand, or possibly there is an erroneous fusion of two adjacent genes.
- Blastx the transcriptome against a protein set, such as Swissprot, or perhaps gene models of a related organism.
blastx -query stringtie.fasta -db uniprot_sprot.fasta -max_target_seqs 10 -evalue 1e-3 > stringtie_vs_swissprot_blastx.tab
- Convert to genomic coordinates, so individual protein hits can be seen spanning exons. The genes
-gcan be defined using the GTF output of StringTie.
blast2genomegff.py -b stringtie_vs_swissprot_blastx.tab -g stringtie.gtf -d uniprot_sprot.fasta -S > stringtie_vs_swissprot_blastx.gff
When running AUGUSTUS, include the options --protein=on --cds=on --gff=on. As above, the proteins themselves (and the CDS nucleotides) can be extracted with the extract_features.py script. Then run either blastp or blastx, for proteins or nucleotide CDS, respectively.
blastp -query renilla_test_prots.fasta -db ~/db/human_uniprot.fasta -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -max_target_seqs 5 > renilla_vs_human_blastp_1e-4.tab
By default, AUGUSTUS does not report exon features (only intron and CDS).
blast2genomegff.py -b renilla_vs_human_blastp_1e-4.tab -g renilla_test_prots.gff -d ~/db/human_uniprot.fasta -S -x > renilla_vs_human_blastp_1e-4.gff
If proteins were used, set -p to blastp. If nucleotide CDS was used, the default -p is blastx.
Blocks of colinear genes between two species can be identified using blast and GFF files of the gene positions for each species.
-btabular blast or diamond results, of the query proteins or genes against some database-qGFF file of the query genes. The results are sensitive to presence of multiple features at the same locus. It is advisable to include only features that would match the blast results, either gene or mRNA. i.e.grep gene annotation.gff > genes_features_only.gff-dGFF of the genes of the target genome
-mminimum length of a block, 3 is usually sufficient for true synteny, as determined by randomized gene order (with-R)-zmax allowed distance between genes. This should be roughly the upper limit of intergenic distances in the genome, meaning 99% of genes are closer than-z(see here for an example).-Rrandomize gene order of the query, to estimate false discovery rate--make-gffproduce a GFF output, instead of gene-by-gene information of the synteny blocks
- Blastx or blastp of the transcriptome (or translated CDS) against a database of proteins from the target species. Use the tabular output
-outfmt 6. A maximum number of sequences does not need to be set, since the objective is to find homology, and this is not assumed from blast similarity. For example, here I am using the genomes of the corals Acropora digitifera and Styllophora pistillata.
blastp -query adi_aug101220_pasa_prot.fa -db Spis.genome.annotation.pep.longest.fa -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-2 > acropora_vs_styllophora_blastp.tab
- Determine the blocks with the
microsynteny.pyscript. Various delimiter parameters may need to be set depending on the version of GFF for the annotations and the names of the proteins. In this case, as the subject proteins contain the same names as theIDfield in the GFF, the delimiter-Dmust be set to any alternate symbol, here using|.
microsynteny.py -b acropora_vs_styllophora_blastp.tab -q test_data/adi_aug101220_pasa_mrna_t1_only.gff -d test_data/Spis.genome.annotation.mrna_only.gff -D "|" > test_data/acropora_vs_styllophora_microsynteny.tab
The standard output is a tab-delimited text file of 11 columns. The colinear block is evident from the systematic numbering of the two genomes, as the five A. digitifera genes (numbered 23536-23540) correspond to the five S. pistillata genes (Spis14158-14162). The strand direction is the same for each gene as well.
query-scaf sub-scaf block-id query-gene q-start q-end q-strand sub-gene s-start s-end s-strand
scaf16952 Spis.scaffold280|size416857 blk-2 aug_v2a.23536.t1 23026 25506 + Spis14158 255619 257861 +
scaf16952 Spis.scaffold280|size416857 blk-2 aug_v2a.23537.t1 28396 43517 + Spis14159 264153 287169 +
scaf16952 Spis.scaffold280|size416857 blk-2 aug_v2a.23538.t1 53236 67680 + Spis14160 294209 310911 +
scaf16952 Spis.scaffold280|size416857 blk-2 aug_v2a.23539.t1 68035 73535 - Spis14161 321061 322080 -
scaf16952 Spis.scaffold280|size416857 blk-2 aug_v2a.23540.t1 77256 88420 + Spis14162 340030 347635 +
There are two main caveats to the data generated by this program. First, the reported block length represents the most genes on either query or target scaffolds, meaning if genes are erronously fused or split on one of the two species, this could, for instance, generate a block of 1 gene in the query and 3 genes in the target. Below is an example of a block where gene aug_v2a.19447.t1 blasts to five genes in a row in S. pistillata. From these data alone, it cannot be determined if the A. digitifera gene is a false fusion, or the S. pistillata genes are falsely split.
scaf11463 Spis.scaffold21|size1341190 blk-19 aug_v2a.19446.t1 188491 189125 - Spis2568 665897 666978 -
scaf11463 Spis.scaffold21|size1341190 blk-19 aug_v2a.19447.t1 192487 193775 - Spis2569 668955 676058 -
scaf11463 Spis.scaffold21|size1341190 blk-19 aug_v2a.19447.t1 192487 193775 - Spis2573.t2 740727 760040 -
scaf11463 Spis.scaffold21|size1341190 blk-19 aug_v2a.19447.t1 192487 193775 - Spis2572 715149 725680 -
scaf11463 Spis.scaffold21|size1341190 blk-19 aug_v2a.19447.t1 192487 193775 - Spis2571 705673 706617 -
scaf11463 Spis.scaffold21|size1341190 blk-19 aug_v2a.19447.t1 192487 193775 - Spis2575 784361 787164 -
The other potential problem occurs in the case of tandem duplications. If a tandem duplication occurred in one of the two genomes, then nearly identical blocks will be identified for each duplicate, as up to 5 intervening genes are allowed (by the option -s). A hypothetical example is shown in the figure below. In such a case, hypothetical genes 1-3 would be matched twice (once normally, once with the intervening gene 1b), meaning the block will be counted twice.
- Optionally, determine the frequency of random matches using the
-Roption. This will randomly reorder the positions of the query proteins, and then check for synteny. Blocks of 3-in-a-row are extremely rare, though blocks of two can be found easily by setting-m 2. This suggests that 3 colinear genes is usually sufficient to infer inherited gene order between the two species. Usually, long blocks are actually erroneous gene fusions in one of the genomes (as above).
microsynteny.py -b acropora_vs_styllophora_blastp.tab -q test_data/adi_aug101220_pasa_mrna_t1_only.gff -d test_data/Spis.genome.annotation.mrna_only.gff -D "|" -R -m 2 > test_data/acropora_vs_styllophora_microsynteny.randomized.tab
- A summary plot of block lengths can be produced using the associated R script
synteny_block_length_plot.R.
Rscript synteny_block_length_plot.R acropora_vs_styllophora_microsynteny.tab
- Generate a GFF of the blocks, to plot in a genome browser. Use the option
--make-gff.
microsynteny.py -b acropora_vs_styllophora_blastp.tab -q test_data/adi_aug101220_pasa_mrna_t1_only.gff -d test_data/Spis.genome.annotation.mrna_only.gff -D "|" > test_data/acropora_vs_styllophora_microsynteny.gff
Generate a PDF of a dot plot, similar to what was done in Srivistava 2008 and Simakov 2013. This requires unidirectional blast results (not reciprocal) as duplicated blocks can be identified this way.
scaffold_synteny.py -b hoilungia_vs_trichoplax_blastp_e-3.tab -q Hhon_BRAKER1_genes.gff3 -d Trichoplax_scaffolds_JGI_AUGUSTUS_transcript_only.gff -f Hhon_final_contigs_unmasked.fasta -F Triad1_genomic_scaffolds.fasta --blast-query-delimiter . --blast-db-delimiter __ -l 80 -L 100 > hoilungia_vs_trichoplax_scaffold2d_points.tab
Then, the R script is run to generate the dot plot. Synteny is clearly evident for major sections of chromosomes, indicated by the diagonals formed by the points. For instance, the longest H. hongkongensis contig maps completely to scaffold 7 in Trichoplax. This is mostly the case for the first 5 contigs in H. hongkongensis.
Rscript synteny_2d_plot.R hoilungia_vs_trichoplax_scaffold2d_points.tab Hoilungia-hongkongensis Trichoplax-adhaerens
The same can be generated for more distant species (such as this one published in Kenny 2020). Here two choanoflagellates are used, Monosiga brevicollis (using the AUGUSTUS reannotation) and Salpingoeca rosetta (at Ensembl).
blastp -query Monbr1_augustus_v1.prot_no_rename.fasta -db Salpingoeca_rosetta.Proterospongia_sp_ATCC50818.pep.all.fa -outfmt 6 -num_threads 6 -evalue 1e-3 -max_target_seqs 100 > monbr1_vs_srosetta_blastp.tab
scaffold_synteny.py -b monbr1_vs_srosetta_blastp.tab -q Monbr1_augustus_v1_no_comment.gff -d ~/genomes/salpingoeca_rosetta/srosetta_mrna_only_ID_renamed.gff -f Monbr1_scaffolds.fasta -F ~/genomes/salpingoeca_rosetta/Salpingoeca_rosetta.Proterospongia_sp_ATCC50818.dna.toplevel.fa.gz -l 40 -L 50 > monbr1_vs_srosetta_scaffold2d_points.tab
Rscript ~/git/genomeGTFtools/synteny_2d_plot.R monbr1_vs_srosetta_scaffold2d_points.tab Monosiga-brevicollis Salpingoeca-rosetta
This is a script to extract feature positions from a GFF to generate a figure that roughly resembles what is seen in a genome browser, to make something that has the same effect as a screenshot but looks better. Because GFFs contain indices by scaffold position, rather than gene, the script effectively converts the tabular GFF to a format where the features are the genes and exons themselves. This allows for easy downstream processing and visualization with the associated script draw_annotation_blocks.R.
-gone or more GFF files, each roughly representing a track in a genome browser-sthe chromosome or scaffold ID-bthe beginning position to extract from that scaffold (inclusive)-ethe end position to extract from that scaffold (also inclusive)
The output of the program is a 5-column tab-delimited file, containing gene name, feature type, start, stop, and strand. Even if multiple GFFs are used, all of the transcripts or genes will end up in the same file.
For example, studying the arrangement of the Lux operon, in the bacterium Aliivibrio fisheri, the genome and GFF are downloaded from NCBI.
extract_coordinates.py -g GCF_000011805.1_ASM1180v1_genomic.gff -s NC_006841.2 -b 1041700 -e 1051700 -p > lux_locus_short_annot.tab
A rather unsophisticated script to plot the extracted coordinates of genes or exons from extract_coordinates.py. By default, it only requires the output of extract_coordinates.py and will generate a .pdf of the same name. In this example, the input file lux_locus_short_annot.tab yields the output lux_locus_short_annot.pdf.
Rscript draw_annotation_blocks.R lux_locus_short_annot.tab
As there is not a straightforward way to display features, or generate a figure of whatever someone would want to convey, the output is rather quirky, ultimately meaning that it is much easier to generate the .pdf and import it into another program like Inkscape.
- The X-axis and scaling of the features is set by the boundaries from
-band-einextract_coordinates.py, meaning to make two graphs to compare loci, the span of-bto-eshould be the same - Each gene or transcript is printed on a different Y-position, of up to 30 features (this can be changed). This means that splice variants are each on their own line, as are genes in operons.
- All features are colored the same.
- The names are taken from the
IDtag in the GFF, which may not be the same asName.
The raw output is shown below. Some feature names are cut off due to the grouping of objects. These can be ungrouped and moved.
Naturally this requires some work to make it presentable, i.e. flipping the axis, coloring each gene, renaming them from the GFF ID, which did not have meaningful IDs for most of the proteins. Thus, a final version may look more like this, maintaining the color scheme used in Dunlap 2009.
This was intended to make a printable version of any NCBI prokaryote genome, and have it displayed on one or more pages, with 1Mbp per page. From the downloaded GFF (or .gz), the PDF is generated automatically with the Rscript.
Rscript draw_genome_annotation.R GCF_000011805.1_ASM1180v1_genomic.gff
From scaffolds or masked contigs, generate a feature for each long repeat of N's or n's (or any other arbitrary letter or pattern). The most obvious application is to make a track for gaps, which is the default behavior. The search is a regular expression, so could be any other simple repeat as well - CACA, CAG (glutamine repeats).
repeat2gtf.py scaffolds.fasta > scaffolds_gaps.gtf
In jbrowse, I typically change a few options in the style to make this more visually useful. The color is set to black, the height is reduced to narrow bars, and the label is the score, which is the length of the gap.
"style" : {
"className" : "feature",
"color" : "#000000",
"height" : 5,
"label" : "score"
},
Convert palindromic repeats from the EMBOSS program palindrome into GTF features. This was meant for mitochondrial genomes, but could potentially be whole nuclear genomes.
To get gene models from blast hits, the best strategy may be to use blast2gff.py with the option -A to convert the blast hits to AUGUSTUS hints (which are in a GFF-like format). This is then specified in the AUGUSTUS run as: --hintsfile=geneset_vs_scaffolds.gff
blast2gff.py -t CDSpart -b geneset_vs_scaffolds.tab -A > geneset_vs_scaffolds.gff
The original idea was intended to take advantage of the speed of blasting. Blast hits are then parsed to give a single command to Genewise, and the gff output is collected into a single file and reformatted for modern genome browsers. This is very similar to the strategy used by the BUSCO pipeline, which takes blast hits and runs AUGUSTUS on the scaffold that was hit. As AUGUSTUS can use HMM-like profiles to find specific proteins that are conserved, perhaps with more complex domain structures, this might be developed further.