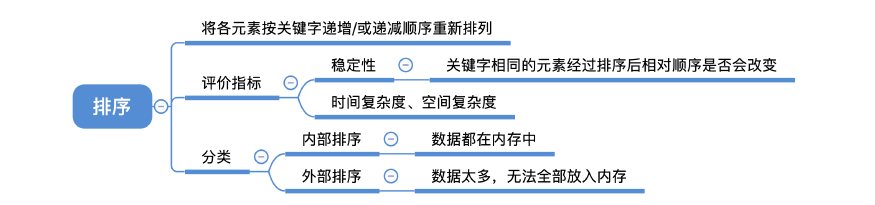
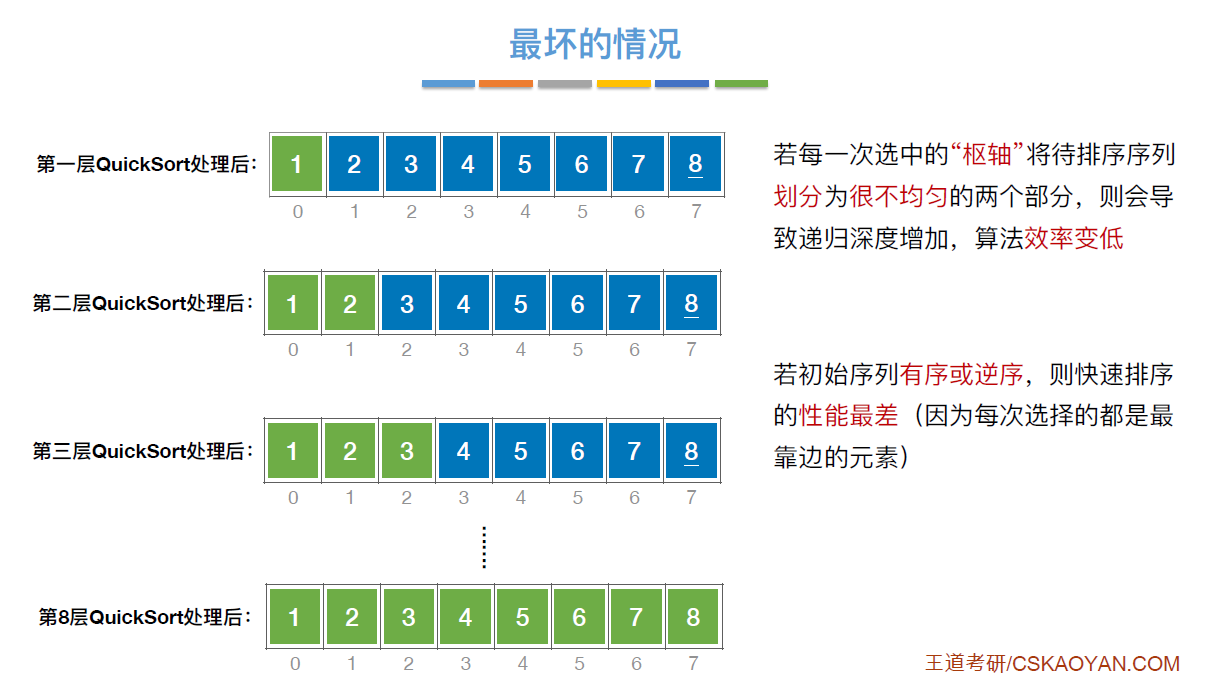
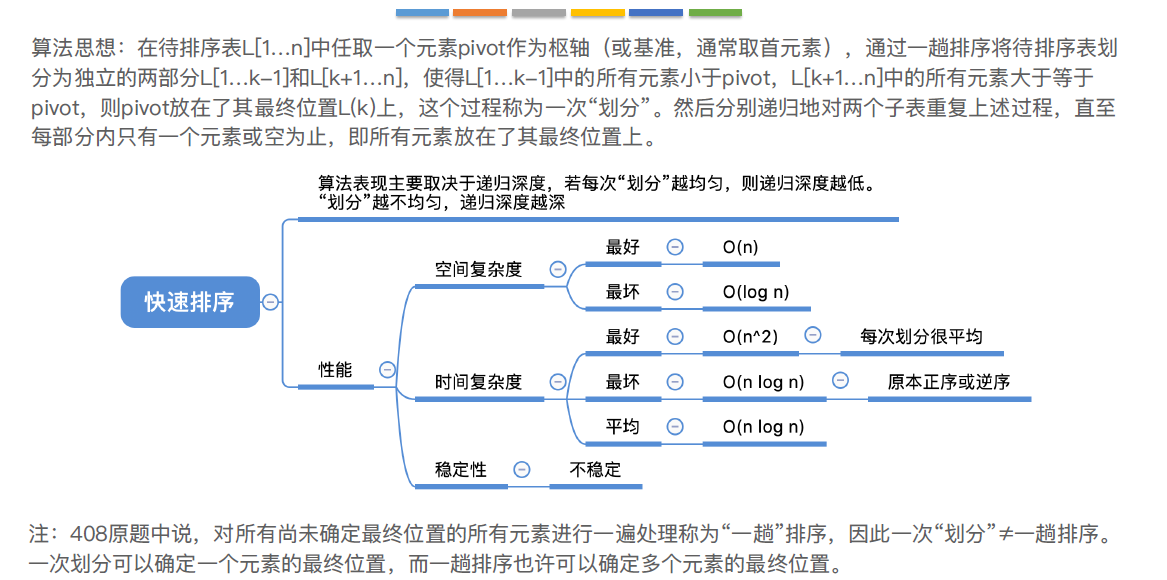
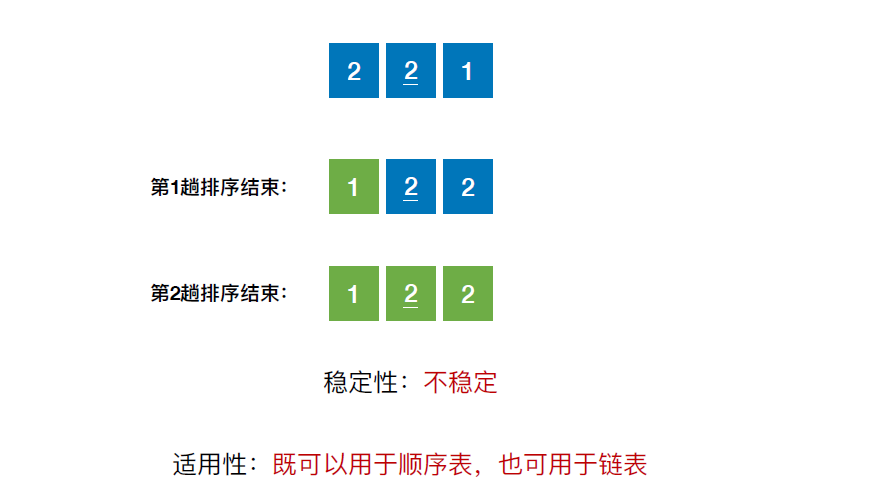
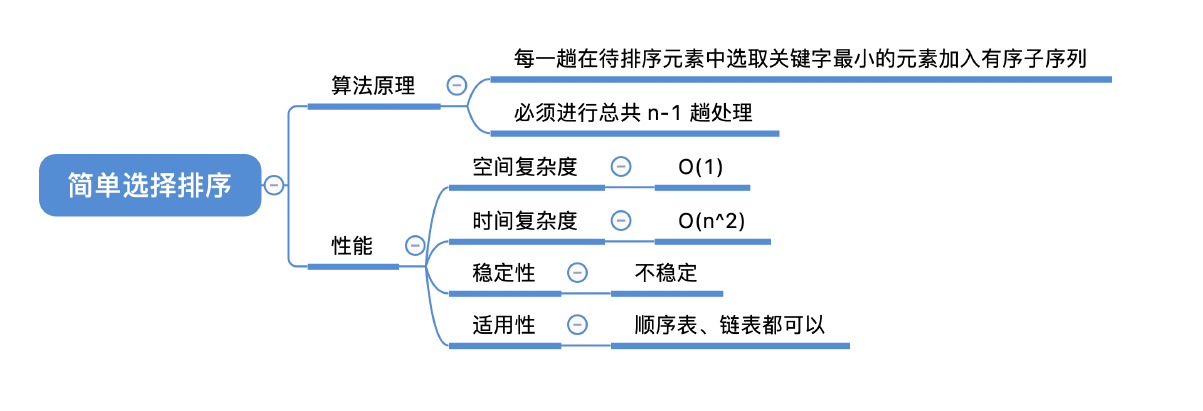
- 时间复杂度
- 空间复杂度
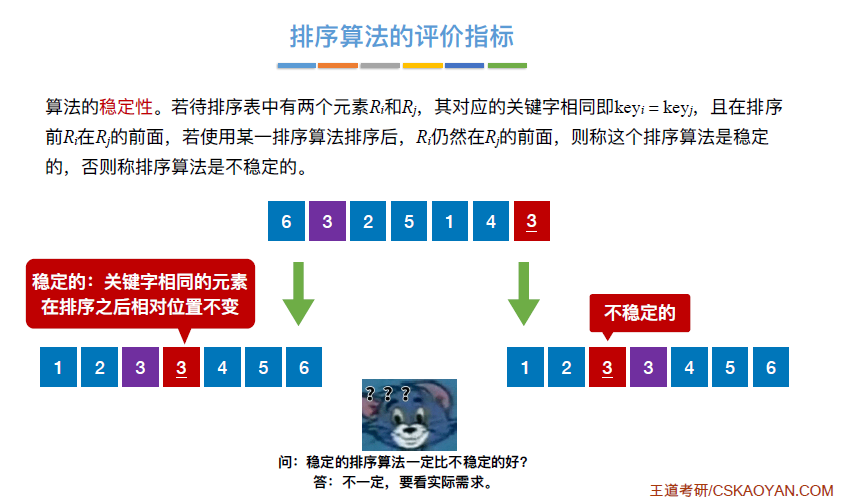
- 稳定性
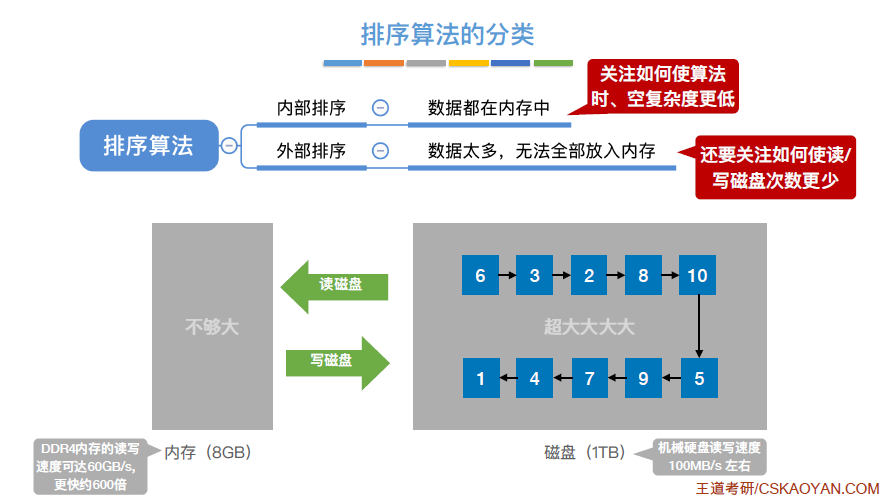
- 内部排序
- 外部排序
//直接插入排序
void InsertSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j, temp;
for(i=1;i<n;i++) //将各元素插入已排好序的序列中
{
if(a[i] < a[i-1]) //若A[i]关键字小于前驱
{
temp = a[i]; //用temp暂存A[i]
for(j=i-1;j>=0 && a[j] > temp;j--) //检查所有前面已排好序的元素
{
a[j+1]=a[j]; //所有大于temp的元素都向后挪位
}
a[j+1]=temp; //复制到插入位置
}
}
}//直接插入排序(带哨兵)
void InsertSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++) //依次将A[2]~A[n]插入到前面已排序序列
{
if(a[i] < a[i-1]) //若A[1]关键码小于其前驱,将A[i]插入有序表
{
a[0] = a[i]; //复制为哨兵,A[0]不存放元素
for(j=i-1;a[0] < a[j]; j--) //从后往前查找待插入位置
{
a[j+1] = a[j]; //向后挪位
}
a[j+1] = a[0]; //复制到插入位置
}
}
}
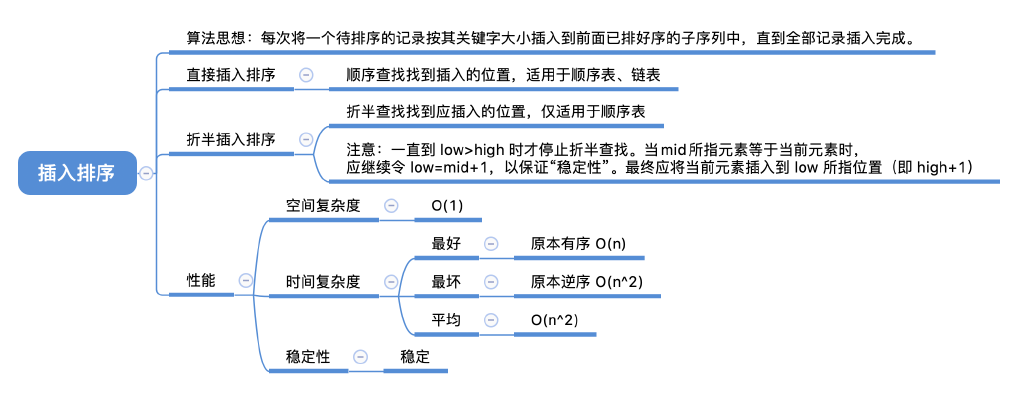
- 当 low > high 时折半查找停止,应将 [low, i - 1] 内的元素全部右移,并将 A[0] 复制到 low 所指位置
- 当 A[mid] = A[0] 时,为了保证算法的“稳定性”,应继续在 mid 所指位置右边寻找插入位置
//折半插入排序
void InsertSort2(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j ,low, mid, high;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++) //依次将a[2]~a[n]插入到前面的已排序序列
{
a[0]=a[i]; //将a[i]暂存到a[0]
low=1;high=i-1; //设置折半查找范围
while(low<=high) //折半查找(默认递增有序)
{
mid = (low+high)/2; //取中间点
if(a[mid] > a[0]) //查找左半子表
{
high = mid-1;
}
else //查找有半子表
{
low = mid+1;
}
for(j=i-1;j>=high+1;j--)
{
a[j+1]=a[j]; //统一后移元素,空出插入位置
}
a[high+1] = a[0]; //插入操作
}
}
}#include <stdio.h>
void printstring(int a[], int n);//打印数组
void InsertSort(int a[], int n);//直接插入排序
void InsertSort1(int a[], int n);//直接插入排序(带哨兵)
void InsertSort2(int a[], int n);//折半插入排序
void main()
{
int a[10]={1,9,0,2,4,2,6,5,8,34};
int b[11]={-1,1,9,0,2,4,2,6,12,8,34};
InsertSort(a, 10);
InsertSort2(b, 11);
printstring(a,10);
printstring(b,11);
}
//打印数组
void printstring(int a[], int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//直接插入排序
void InsertSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j, temp;
for(i=1;i<n;i++) //将各元素插入已排好序的序列中
{
if(a[i] < a[i-1]) //若A[i]关键字小于前驱
{
temp = a[i]; //用temp暂存A[i]
for(j=i-1;j>=0 && a[j] > temp;j--) //检查所有前面已排好序的元素
{
a[j+1]=a[j]; //所有大于temp的元素都向后挪位
}
a[j+1]=temp; //复制到插入位置
}
}
}
//直接插入排序(带哨兵)
void InsertSort1(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++) //依次将A[2]~A[n]插入到前面已排序序列
{
if(a[i] < a[i-1]) //若A[1]关键码小于其前驱,将A[i]插入有序表
{
a[0] = a[i]; //复制为哨兵,A[0]不存放元素
for(j=i-1;a[0] < a[j]; j--) //从后往前查找待插入位置
{
a[j+1] = a[j]; //向后挪位
}
a[j+1] = a[0]; //复制到插入位置
}
}
}
//折半插入排序
void InsertSort2(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j ,low, mid, high;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++) //依次将a[2]~a[n]插入到前面的已排序序列
{
a[0]=a[i]; //将a[i]暂存到a[0]
low=1;high=i-1; //设置折半查找范围
while(low<=high) //折半查找(默认递增有序)
{
mid = (low+high)/2; //取中间点
if(a[mid] > a[0]) //查找左半子表
{
high = mid-1;
}
else //查找有半子表
{
low = mid+1;
}
for(j=i-1;j>=high+1;j--)
{
a[j+1]=a[j]; //统一后移元素,空出插入位置
}
a[high+1] = a[0]; //插入操作
}
}
}
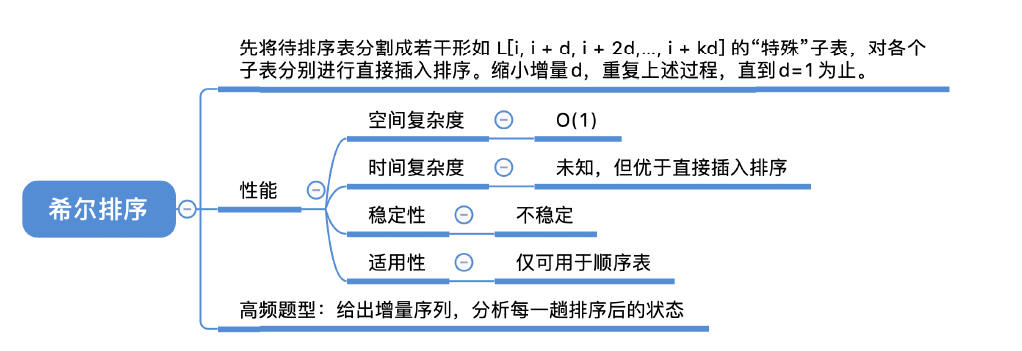
- 希尔排序:先追求表中元素部分有序,再逐渐逼近全局有序
- 时间复杂度:和增量序列d,d2,d3…的选择有关,目前无法用数学手段证明确切的时间复杂度最坏时间复杂度为O(n^2),当n在某个范围内时,可达O(n^13)
- 适用性:仅适用于顺序表,不适用于链表
#include <stdio.h>
void printstring(int a[], int n);//打印数组
void Shellsort(int a[], int n);//希尔排序
void main()
{
int b[11]={-1,1,9,0,2,4,2,6,12,8,34};
Shellsort(b, 11);
printstring(b,11);
}
//打印数组
void printstring(int a[], int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//希尔排序
void Shellsort(int a[], int n)
{
int i,j,d;
//a[0]只是暂存单元,不是哨兵,当j<=0时,插入位置已到
for(d=n/2;d>=1;d=d/2) //步长变化
{
for(i=d+1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i] < a[i-d]) //需将a[i]插入有序增量子表
{
a[0] = a[i]; //暂存在a[0]中
for(j=i-d;j>0 && a[0]<a[j];j-=d)
{
a[j+d] = a[j]; //记录后移,查找插入的位置
}
a[j+d] = a[0]; //插入
}//if
}
}
}知识回顾与重要考点
#include <stdio.h>
//交换两个元素的值
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
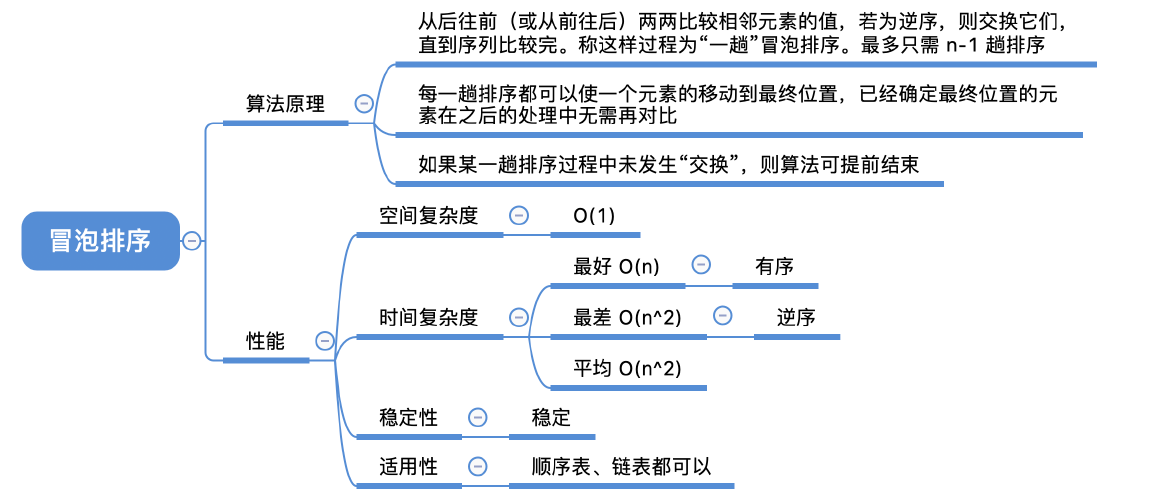
void BubbleSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
int flag=0; //表示本趟冒泡是否发生交换的标志
for(j=n-1;j>i;j--) //一趟冒泡过程
{
if(a[j] < a[j-1]) //若为逆序
{
swap(&a[j-1], &a[j]); //交换
flag=1;
}
}
if(flag==0) //本趟遍历没有发生交换,说明表已经有序
return;
}
}
void main()
{
int a[10]={10,5,0,9,2,7,4,7,2,40};
BubbleSort(a,10);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}知识回顾与重要考点
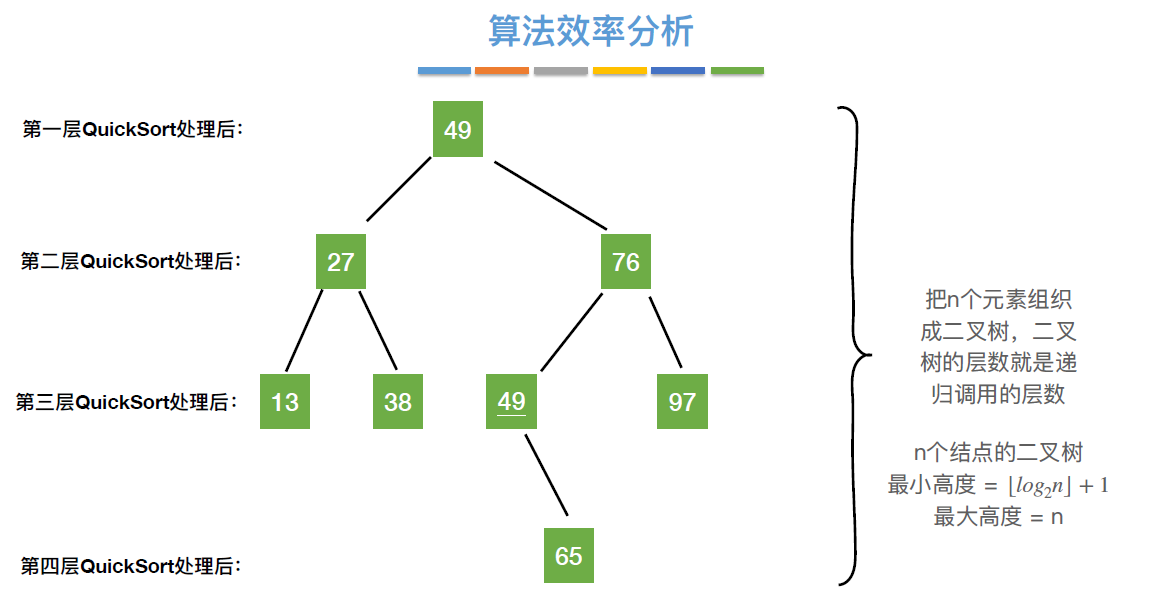
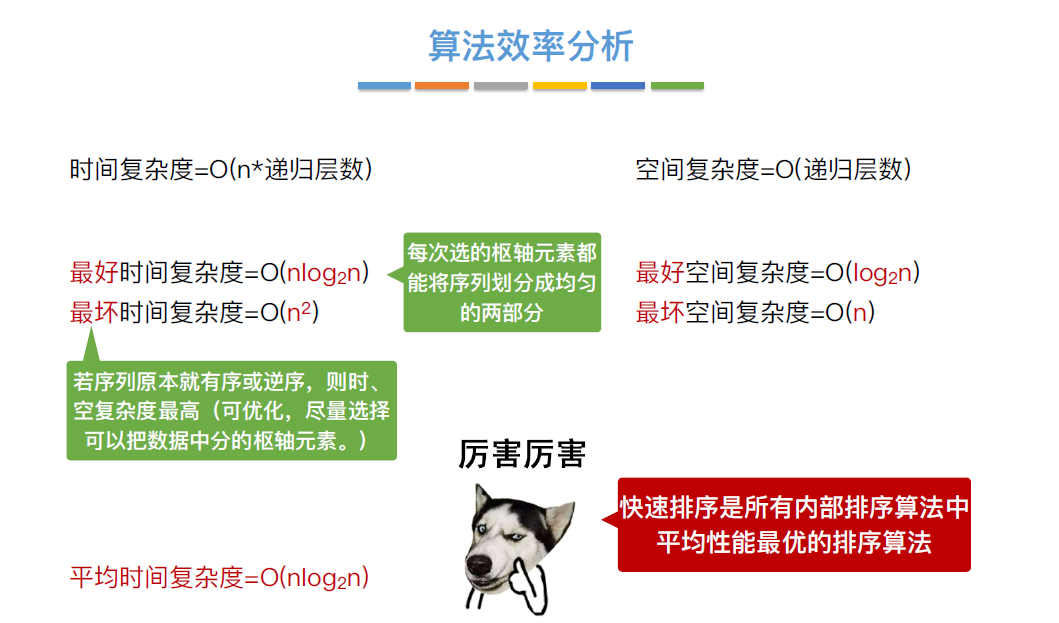
#include <stdio.h>
//用第一个元素将待排序序列划分成左右两个部分
int Partition(int a[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot=a[low]; //第一个元素作为枢轴
while(low < high) //用low、high搜索枢轴的最终位置
{
while(low < high && a[high] >= pivot) high--;
a[low] = a[high]; //比枢轴小的元素移到到左端
while(low < high && a[low] <= pivot) low++;
a[high] = a[low]; //比枢轴大的元素移到到右端
}
a[low] = pivot; //枢轴元素存放到最终位置
return low; //返回存放枢轴的最终位置
}
//快速排序
void QuickSort(int a[], int low, int high)
{
if(low < high) //递归跳出的条件
{
int pivotpos = Partition(a, low, high);//划分
QuickSort(a, low, pivotpos-1); //划分左子表
QuickSort(a, pivotpos+1, high); //划分右子表
}
}
void main()
{
int a[10]={10,29,0,1,23,45,8,4,2,1};
QuickSort(a, 0, 9);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}选择排序:每一趟在待排序元素中选取关键字最小(或最大)的元素加入有序子序列
#include <stdio.h>
void printstring(int a[], int n);//打印数组
void SelectSort(int a[], int n);//简单选择排序
void main()
{
int b[11]={-1,1,9,0,2,4,2,6,12,8,34};
SelectSort(b, 11);
printstring(b,11);
}
//打印数组
void printstring(int a[], int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//简单选择排序
void SelectSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++) //一共进行n-1趟
{
int min = i; //记录最小元素的位置
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++) //在a[i...n-1]中选择最小的元素
{
if(a[min] > a[j]) //更新最小元素的位置
{
min = j;
}
}
if(min != i) //交换元素位置,共移动元素3次
{
int temp = a[min];
a[min] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
}稳定性:不稳定
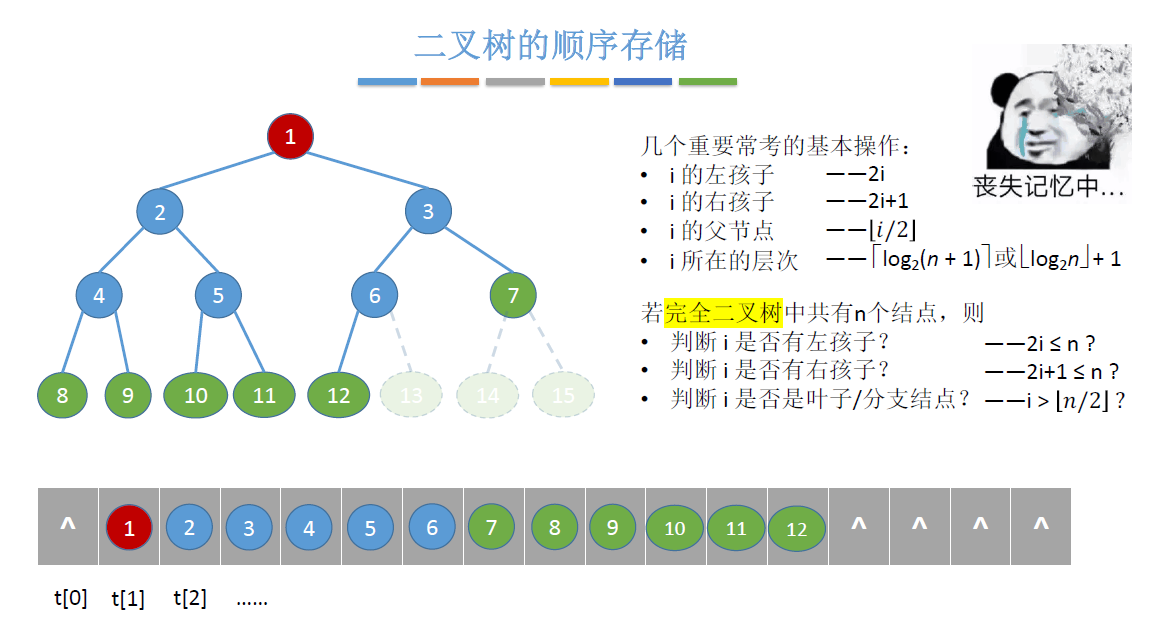
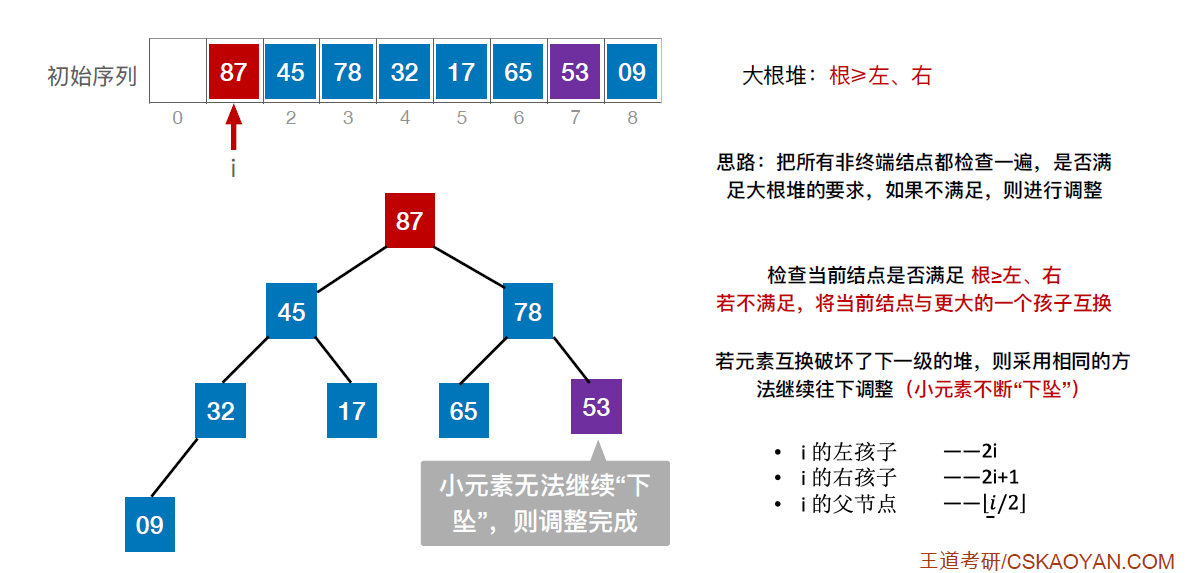
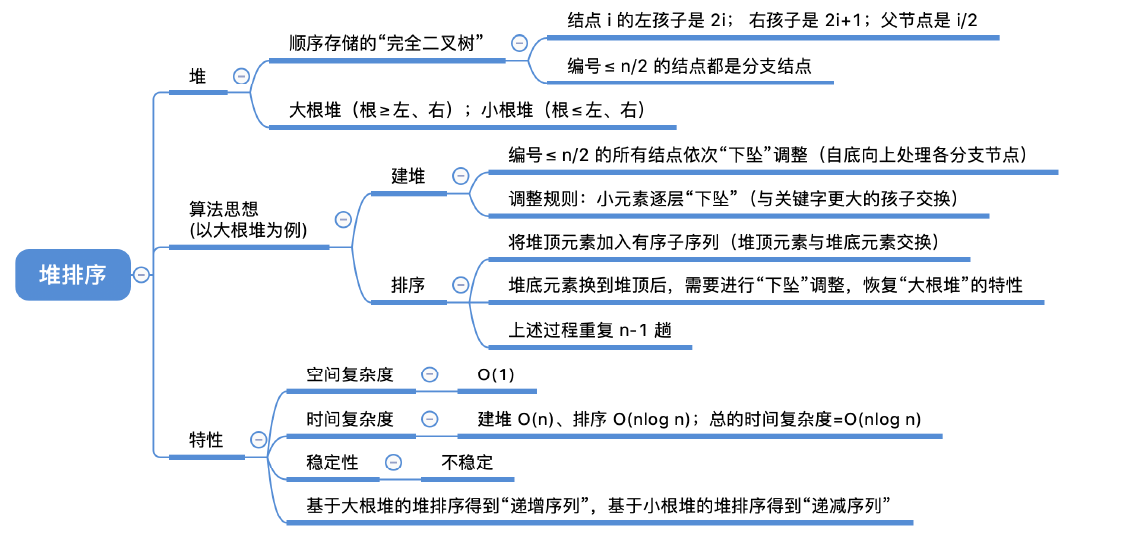
#include <stdio.h>
//将以k为根的子树调整为大根堆
void HeadAdjust(int a[],int k,int len)
{
a[0] = a[k]; //a[0]暂存子树的根结点
for(int i=2*k;i<=len;i*=2) //沿着key较大的子结点向下筛选
{
if(i<len&&a[i]<a[i+1]) //取得key较大的子结点的下标
{
i++;
}
if(a[0] >= a[i]) //筛选结果
{
break;
}
else
{
a[k] = a[i]; //将a[i]调整到双亲结点上
k = i; //修改k值,以便继续向下筛选
}
}
a[k] = a[0]; //被筛选结点的值放入最终位置
}
//建立大根堆
void BuildMaxHeap(int a[],int len)
{
for(int i=len/2;i>0;i--) //从后往前调整所有非终端结点
{
HeadAdjust(a,i,len);
}
}
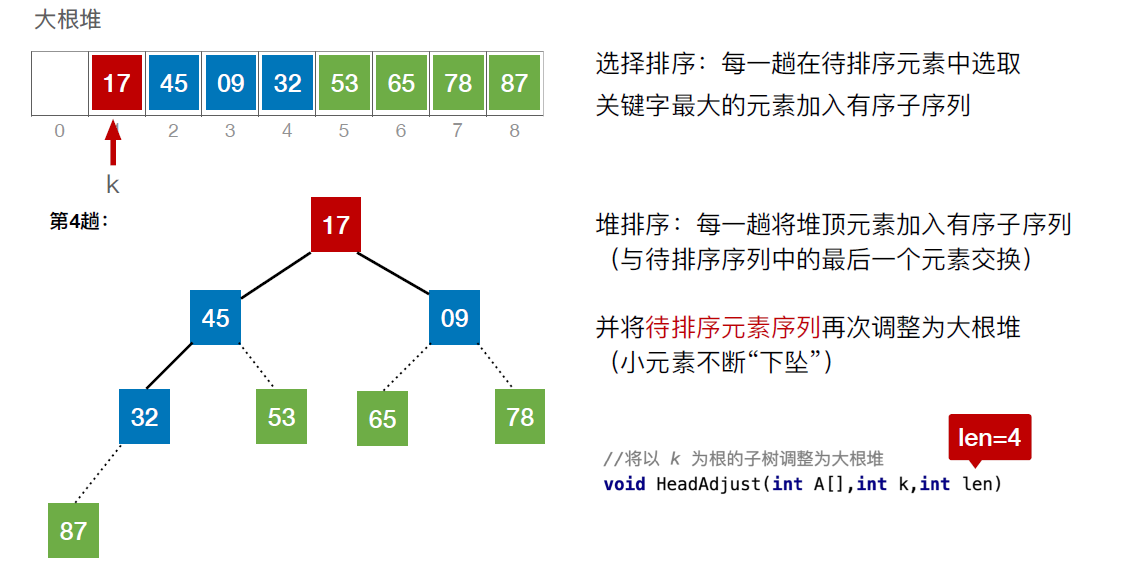
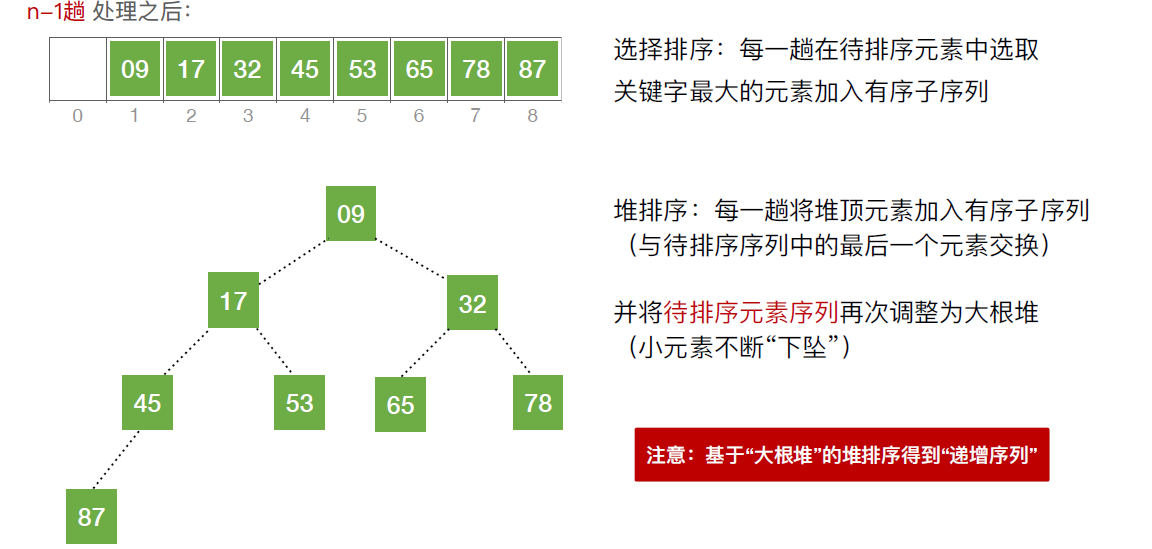
//堆排序的完整逻辑
void HeapSort(int a[],int len)
{
BuildMaxHeap(a,len); //建立初始的堆
for(int i=len;i>1;i--) //n-1趟的交换和建堆过程
{
int temp = a[i]; //堆顶元素和堆底元素交换
a[i] = a[1];
a[1] = temp;
HeadAdjust(a,1,i-1); //把剩余的待排序元素整理成堆
}
}
void main()
{
int a[11]={0,10,29,0,1,23,45,8,4,2,1};
HeapSort(a, 10);
for(int i=0;i<11;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
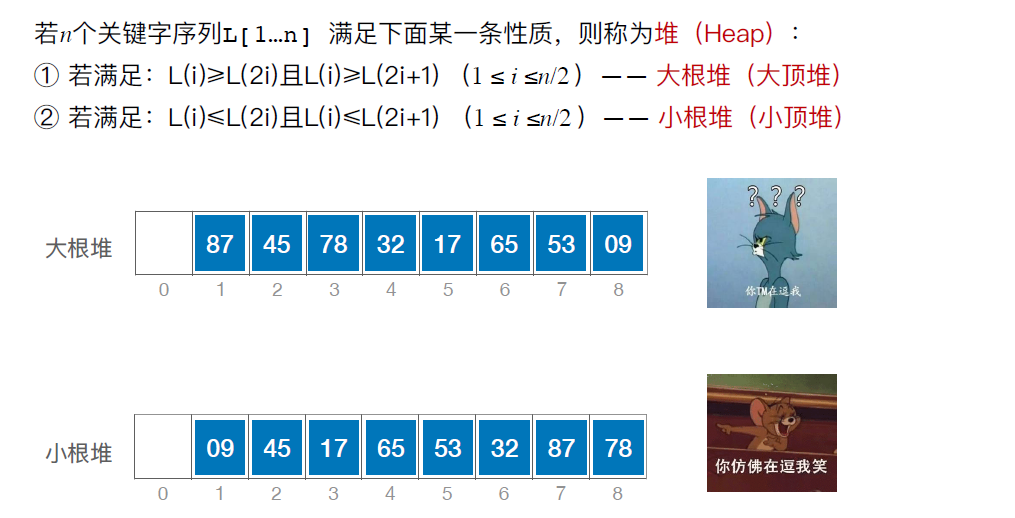
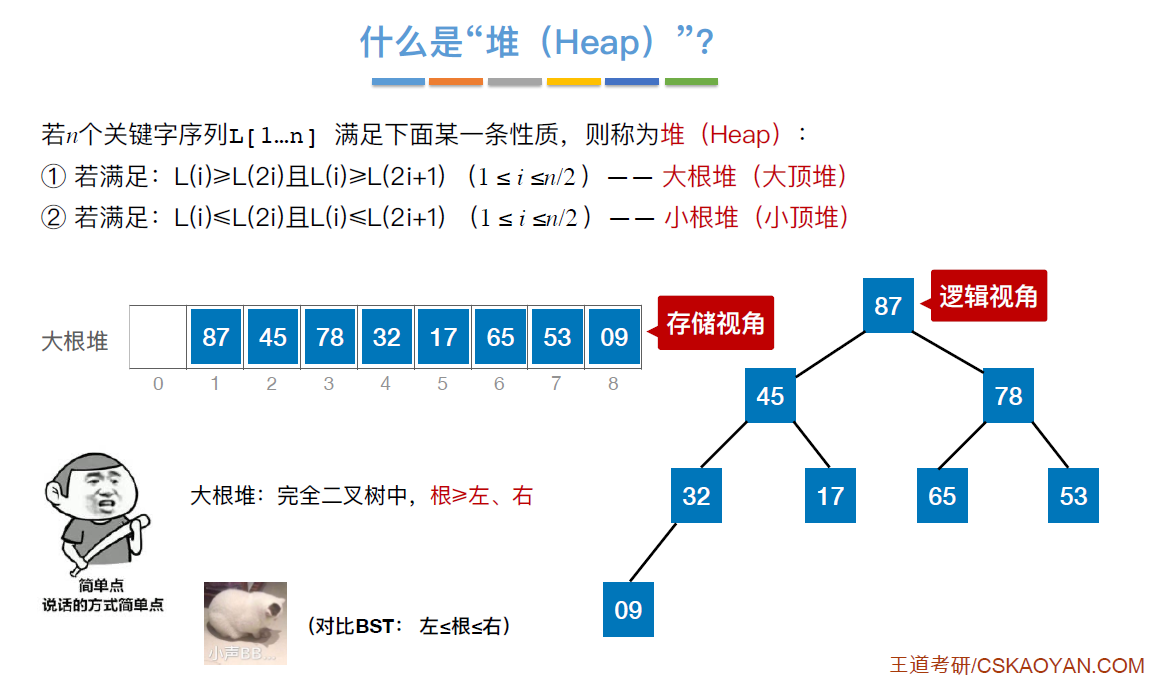
}以小根堆为例:
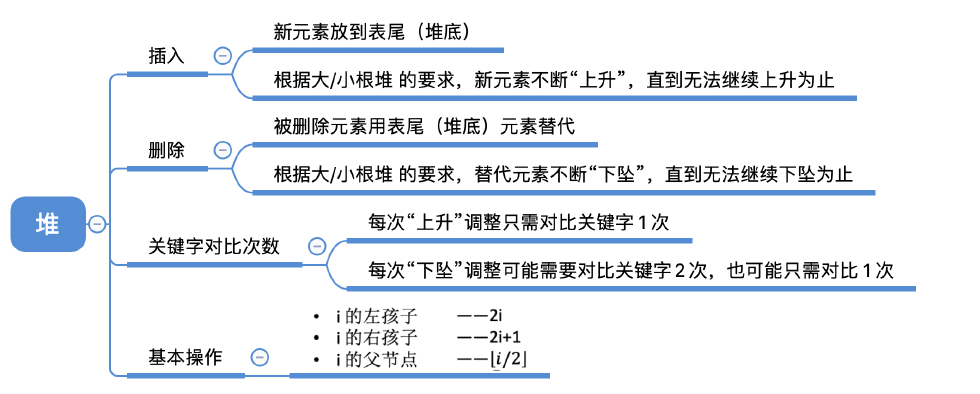
对于小根堆,新元素放到表尾,与父节点对比,若新元素比父节点更小,则将二者互换。新元素就这样一路“上升”,直到无法继续上升为止
以小根堆为例:
被删除的元素用堆底元素替代,然后让该元素不断“下坠”,直到无法下坠为止
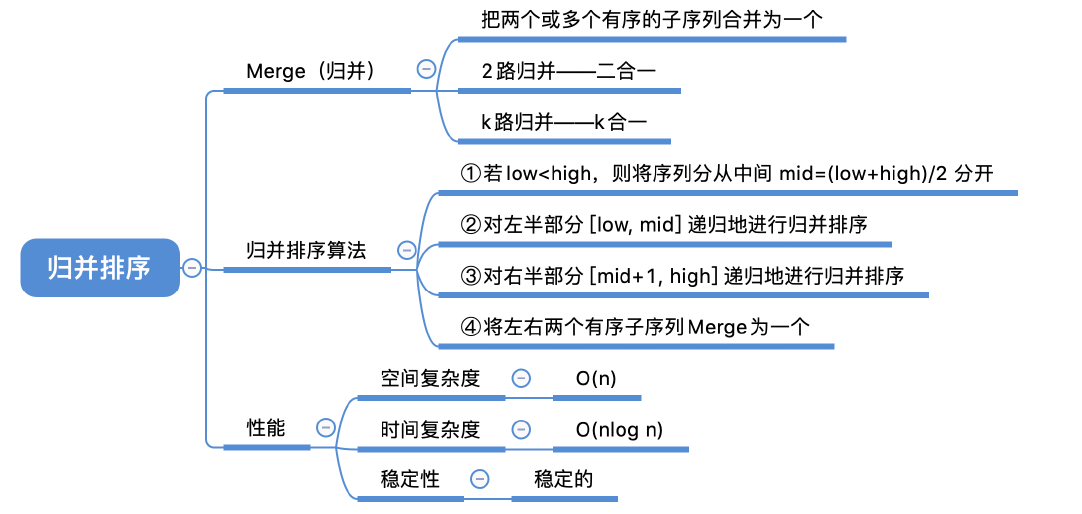
#include <stdio.h>
int b[11];
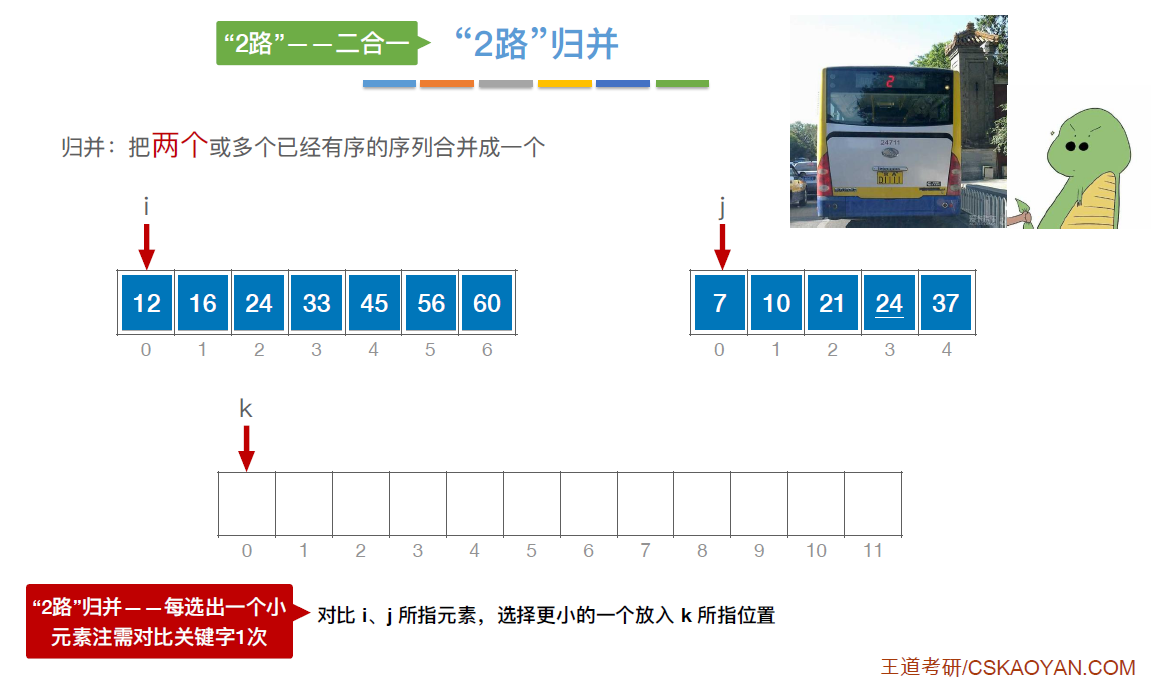
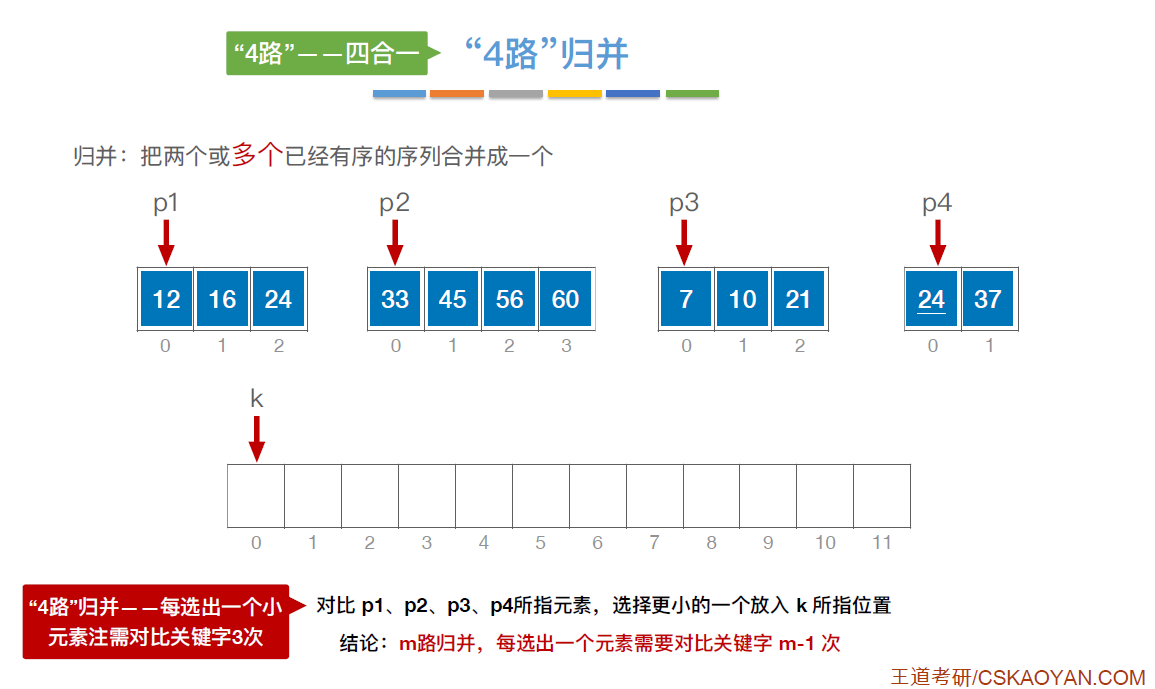
//a[low...mid]和a[mid+1...high]各自有序,将两个部分归并
void Merge(int a[],int low,int mid,int high)
{
int i,j,k;
for(k=low;k<=high;k++)
{
b[k] = a[k]; //将a中所有元素复制到b中
}
for(i=low,j=mid+1,k=i;i<=mid&&j<=high;k++)
{
if(b[i] <= b[j])
{
a[k] = b[i++]; //将最小值复制到a中
}
else
{
a[k] = b[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid) a[k++] = b[i++];
while(j<=high) a[k++] = b[j++];
}
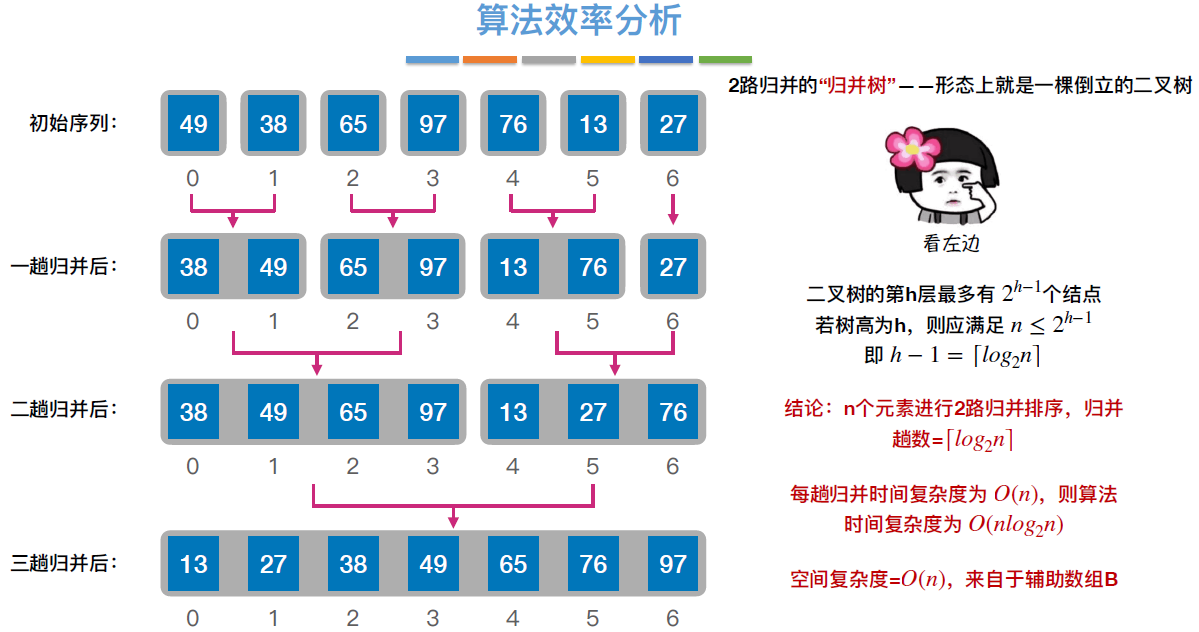
void MergeSort(int a[],int low,int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2; //从中间划分
MergeSort(a,low,mid); //对左半部分归并排序
MergeSort(a,mid+1,high); //对右半部分归并排序
Merge(a,low,mid,high); //归并
}
}
void main()
{
int a[10]={10,2,1,9,6,7,5,0,3,2};
MergeSort(a,0,9);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}