Topics:
- Linked Lists
- Queues
- Binary Search Trees
- Heaps
-
Implement each data structure, starting with the linked list data structure. Make sure you're in the approriate directory, then run
python3 test_[NAME OF DATA STRUCTURE].pyto run the tests for that data structure and check your progress. Get all the tests passing for each data structure. -
Open up the
Data_Structures_Questions.mdfile, which asks you to evaluate the runtime complexity of each of the methods you implemented for each data structure. Add your answers to each of the questions in the file.
- Should have the methods:
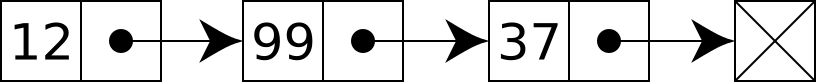
add_to_tail,remove_head,contains, andget_max.add_to_tailreplaces the tail with a new value that is passed in.remove_headremoves and returns the head node.containsshould search through the linked list and return true if a matching value is found.get_maxreturns the maximum value in the linked list.
- The
headproperty is a reference to the first node and thetailproperty is a reference to the last node. Build your nodes with objects.
- Should have the methods:
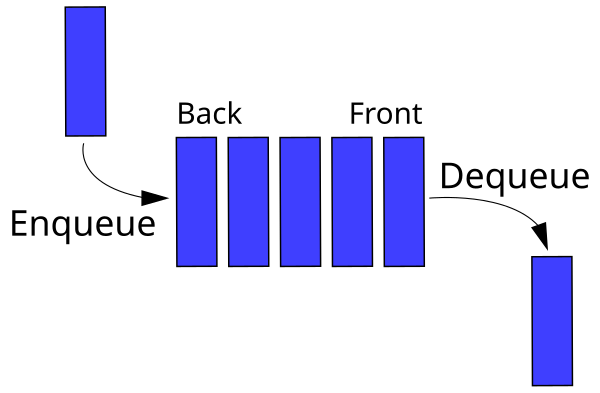
enqueue,dequeue, andlen.enqueueshould add an item to the back of the queue.dequeueshould remove and return an item from the front of the queue.lenreturns the number of items in the queue.
- Should have the methods
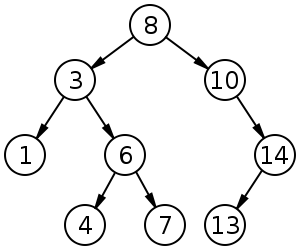
insert,contains,get_max.insertadds the input value to the binary search tree, adhering to the rules of the ordering of elements in a binary search tree.containssearches the binary search tree for the input value, returning a boolean indicating whether the value exists in the tree or not.get_maxreturns the maximum value in the binary search tree.
- Should have the methods
insert,delete,get_max,_bubble_up, and_sift_down.insertadds the input value into the heap; this method should ensure that the inserted value is in the correct spot in the heapdeleteremoves and returns the 'topmost' value from the heap; this method needs to ensure that the heap property is maintained after the topmost element has been removed.get_maxreturns the maximum value in the heap in constant time._bubble_upmoves the element at the specified index "up" the heap by swapping it with its parent if the parent's value is less than the value at the specified index._sift_downgrabs the indices of this element's children and determines which child has a larger value. If the larger child's value is larger than the parent's value, the child element is swapped with the parent.
-
Implement a doubly-linked list class that adheres to the following specification. Uncomment the tests in the
tests/doubly-linked-list.test.jsfile in order to test your solution.-
Consists of a
DoublyLinkedListclass and aListNodeclass. -
The
ListNodeclass has the methodsinsert_after,insert_before, anddelete.insert_afterinserts a new node with the input value after the calling node.insert_beforeinserts a new node with the input value before the calling node.deleteshould remove the calling node from the list (think about what that means).
-
The
DoublyLinkedListclass, like theLinkedListclass, holds references to theheadof the list as well as thetail; it has the methodsadd_to_head,remove_from_head,add_to_tail,remove_from_tail,move_to_front,move_to_back, anddeleteadd_to_headcreates a new node with the input value and adds the new node as the new head of the list.add_to_tailcreates a new node with the input value and adds the new node as the new tail of the list.remove_from_headremoves the current head of the list; the current head's next node should be designated as the new head.remove_from_tailremoves the current tail of the list; the current tail's previous node should be designated as the new tail.move_to_frontreceives a node and moves that node (if it exists in the list) to the front of the list as the new head.move_to_endreceives a node and moves that node (if it exists in the list) to the back of the list as the new tail.deletereceives a node as input and deletes that node from the list.
-