- Advantages
- Live demos
- How it works
- Simple usage
- Performance comparison
- Attentions
- Props type
- Public methods
- Contributions
- Changelogs
-
Items are independent.
-
Tiny and very easy to use.
-
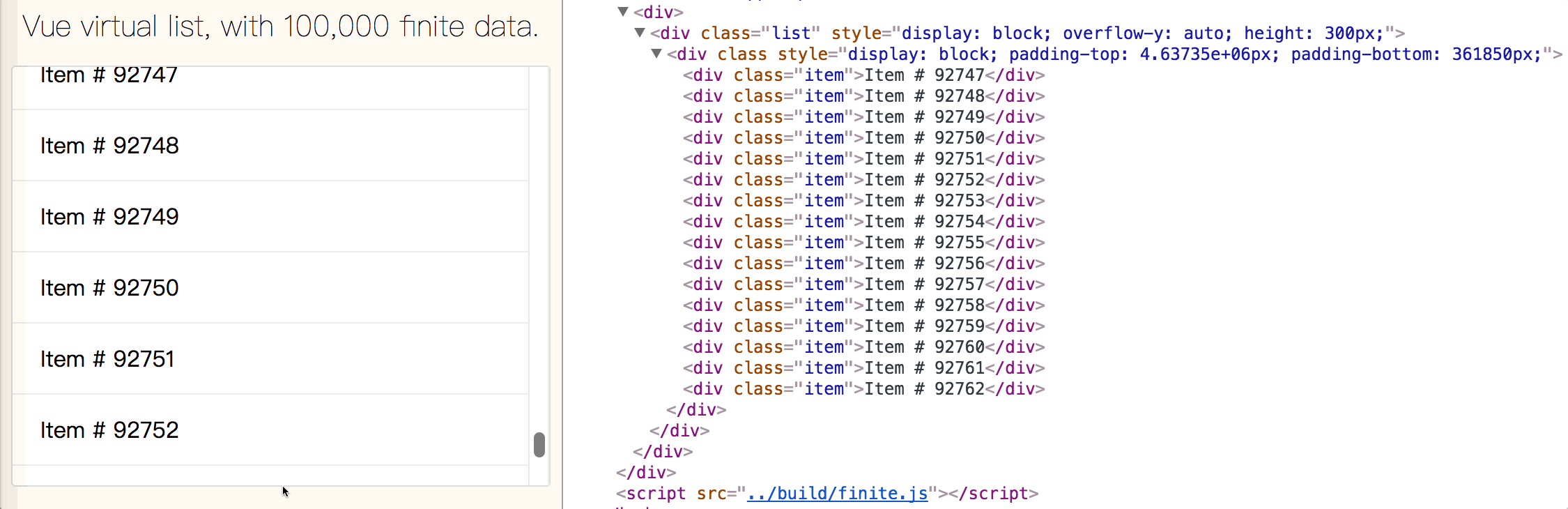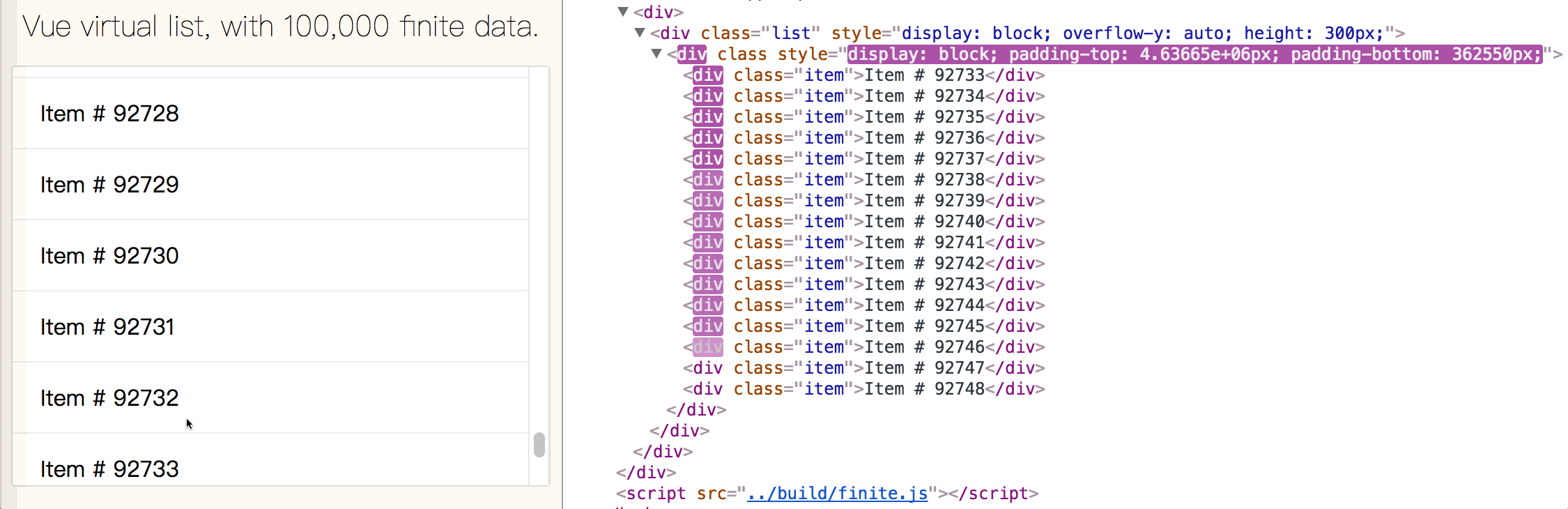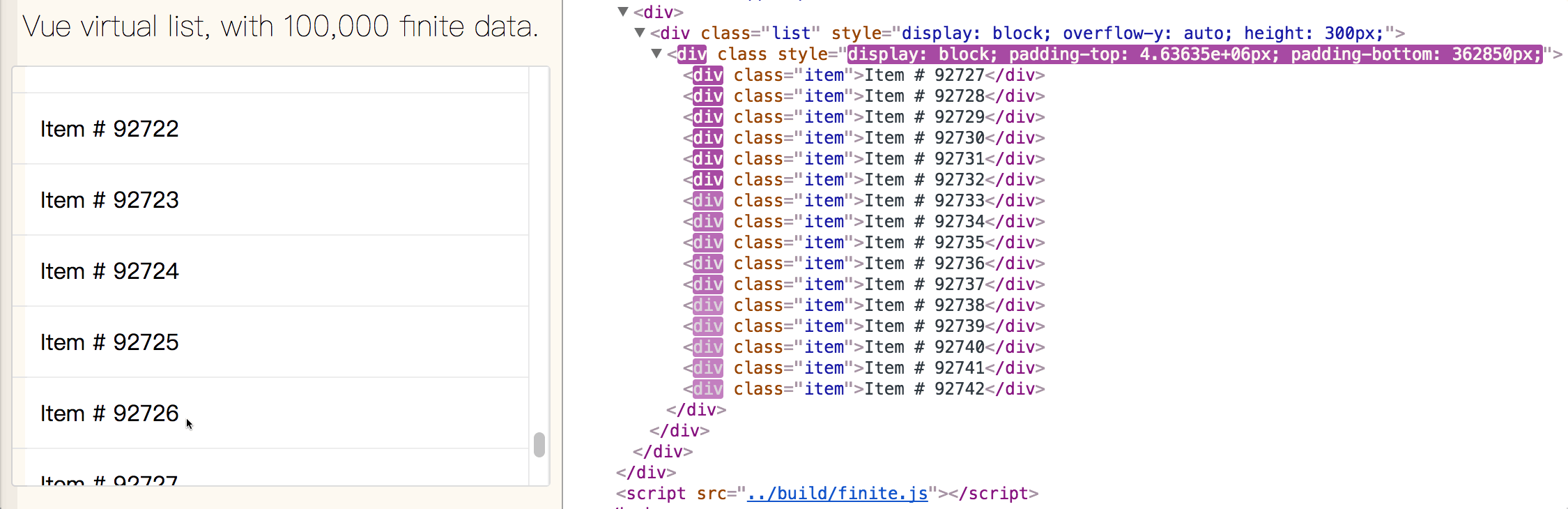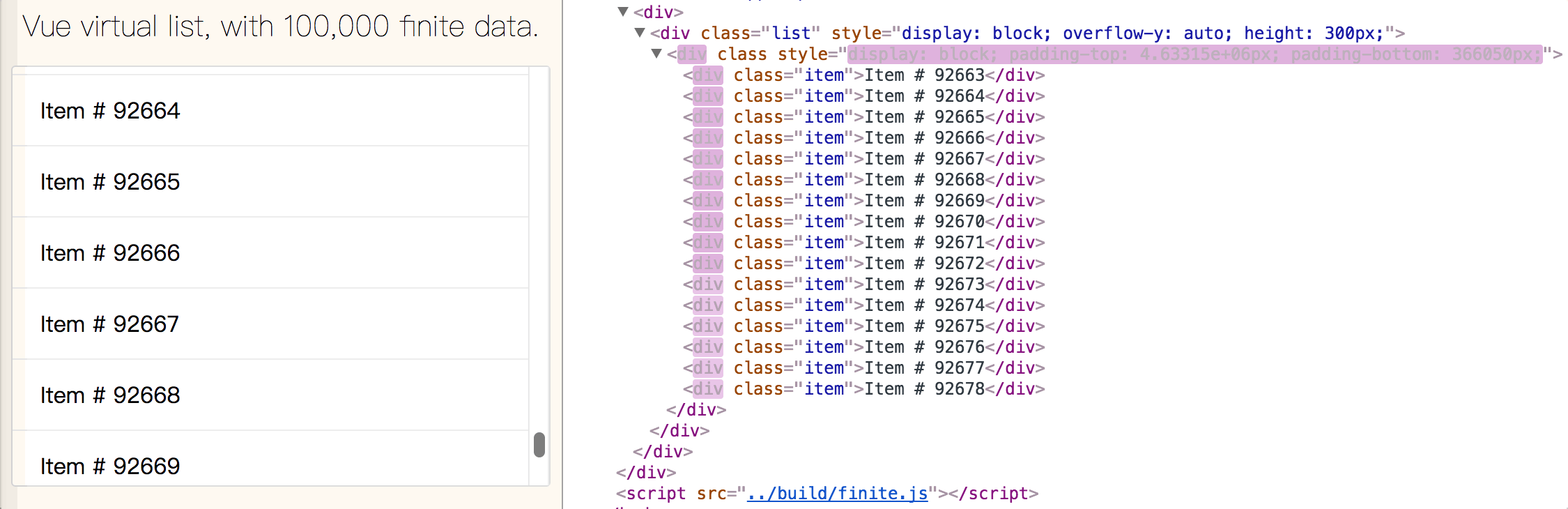
Big data list with high performance.
The main difference between item-mode and vfor-mode is that: item-mode make a higher performance but not very convenient to handle changing data frequently; however, vfor-mode is just the opposite.
Besides, you can also compare the experience which without using virtual-list here: without-virtual-list.
npm install vue-virtual-scroll-list --saveAll you need to care about is only data!
<template>
<div>
<virtual-list :size="40" :remain="8">
<item v-for="item of items" :key="item.id" />
</virtual-list>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import item from '../item.vue'
import virtualList from 'vue-virtual-scroll-list'
export default {
data () {
return {
items: [ {id: 1}, {id: 2}, {id: 3}, ... ]
}
},
components: { item, 'virtual-list': virtualList }
}
</script>This mode can save a considerable amount of memory and performance. Props item, itemcount and itemprops are both required, you don't need put <item/> with a v-for directive inside virtual-list, just assign it as prop item:
<template>
<div>
<virtual-list :size="40" :remain="8"
:item="item"
:itemcount="100000"
:itemprops="getItemprops"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import itemComponent from '../item.vue'
import virtualList from 'vue-virtual-scroll-list'
export default {
data () {
return {
item: itemComponent,
}
},
methods: {
getItemprops (itemIndex) {
const itemProps = getItemProp(itemIndex)
return {
// <item/> will render with itemProps.
// https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html#createElement-Arguments
props: itemProps
}
}
},
components: { 'virtual-list': virtualList }
}
</script>
Whenever you want to change any item data from list in this mode, you need call public method forceRender() after source data change. Increase or decrease items, you need to keep itemcount and call forceRender() together.
Using variable height, props remain and size is still required. All the index variable height and scroll offset will be cached by virtual-list after the binary-search calculate, if you want to change anyone <item/> height from data, you need call public method updateVariable(index) to clear the offset cache.
If you assign variable as true, do not set inline style height inside <item/> component, you must set inline style height on <item/> component outside directly, such as:
<template>
<div>
<virtual-list :size="40" :remain="8" :variable="true">
<item v-for="item of items" :key="item.id" :style="{ height: item.height + 'px' }" />
</virtual-list>
</div>
</template>More use ways or getting start you can refer to these clearly demos or test suites.
According to the demos above, here are lists of approximate statistics:
| Build amount | item-mode | vfor-mode | without virtual list |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 8 ms | 35 ms | 220 ms |
| 10,000 | 10 ms | 170 ms | 1500 ms |
| 100,000 | 20 ms | 1300 ms | Browser crash! |
| Build amount | item-mode | vfor-mode | without virtual list |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 10 MB | 80 MB | 200 MB |
| 10,000 | 25 MB | 120 MB | 220 MB |
| 100,000 | 55 MB | 550 MB | Browser crash! |
-
Must assign the
:keyproperty on<item>component or dom frag withv-fordirective. -
Consider using
box-sizing: border-boxon<item>if you want absolutely correct scroll height.
| Prop | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
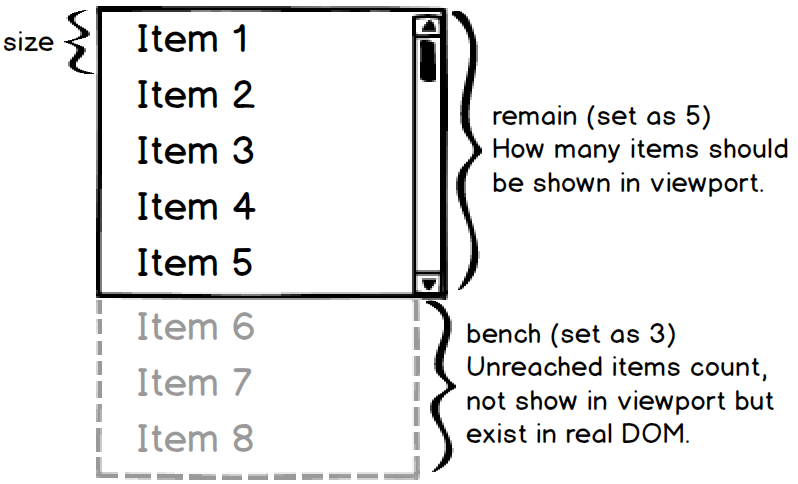
| size | Number | ✓ | Each list item height, in variable height, this prop just use to calculate the virtual-list outside container viewport fixed height. |
| remain | Number | ✓ | How many items should be shown in virtual-list viewport, so size and remain determine the outside container viewport height (size × remian). |
| bench | Number | * | Default value is equal to remain, unreached items count, not show in virtual-list viewport but exist in real DOM, the larger the bench, the higher the scroll performance will achieved. |
| start | Number | * | Default value is 0, the initial scroll start index. It must be integer and in the range of list index, if invalid there will be effected as 0 or the last one. |
| offset | Number | * | Default value is 0, the initial scroll offset. If both start and offset are assigned at initialization, start is preferred. |
| debounce | Number | * | It's disabled by default, milliseconds of using debounce function to ensure scroll event doesn't fire so often that it bricks browser performance. |
| rtag | String | * | Default value is div, the virtual-list root element tag name, in all cases it's style is set to display: block; |
| wtag | String | * | Default value is div, the virtual-list item wrapper element tag name, in all cases it's style is set to display: block; |
| wclass | String | * | Default is no classname, the virtual-list item wrapper element class, if assign this prop, you better not to change it's CSS box model. |
| pagemode | Boolean | * | Let virtual-list scroll with page viewport. |
| totop | Function | * | Called when virtual-list is scrolled to top, no param. |
| tobottom | Function | * | Called when virtual-list is scrolled to bottom, no param. |
| onscroll | Function | * | Called when virtual-list is scrolling, with param: (event, data). |
| variable | Function or Boolean | * | Used in variable height, if assign Function, this prop is a variable height getter function which is called with param: (index) when each item is ready to be calculated; if assign Boolean, virtual-list will get each item variable height by it's inline style height automatic. |
| item | Component | * | Using in item-mode, list item vue component. |
| itemcount | Number | * | Using in item-mode, list data total counts. |
| itemprops | Function | * | Using in item-mode, a function call when each item is going to be rendered. |
Here are some usefull public methods you can call via ref:
-
forceRender(): force render virtual-list if you need or make it refresh. -
updateVariable(index): update item height by index in variable height list.
Welcome to improve vue-virtual-scroll-list with any issue, pull request or code review.
Maintain and update occasionally, for changes see release.