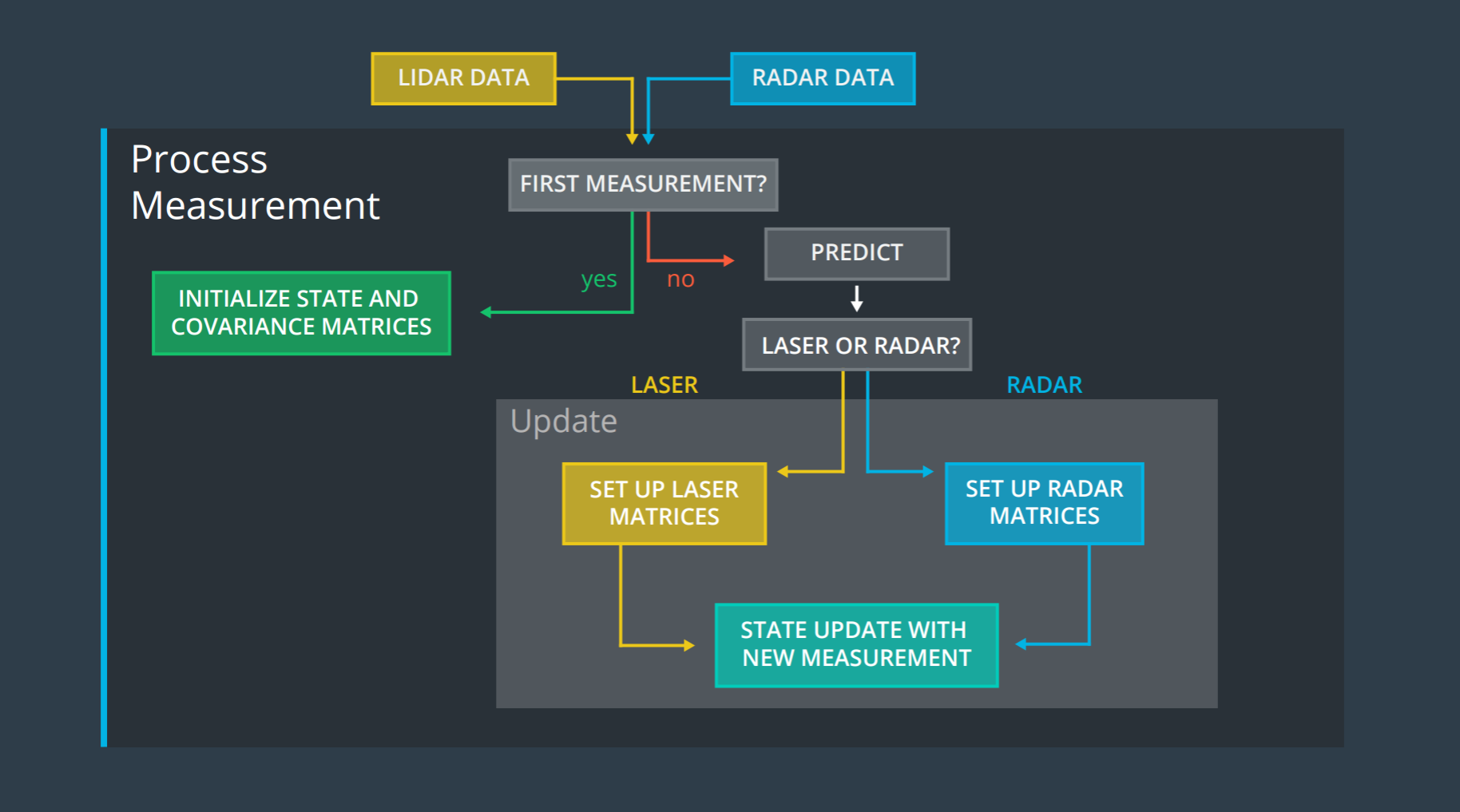
In this project, I implemented an Extended Kalman Filter in C++ language. The simulator provided by the Udacity generates noisy LIDAR and RADAR measurements of the position and velocity of an object and using my EKF implementation I performed a sensor fusion of the LIDAR and RADAR data to predict the positiona dn velocity of the object.
Here is the EKF map shown :
This project involves the Term 2 Simulator which can be downloaded here
This repository includes two files that can be used to set up and install uWebSocketIO for either Linux or Mac systems. For windows you can use either Docker, VMware, or even Windows 10 Bash on Ubuntu to install uWebSocketIO. Please see the uWebSocketIO Starter Guide page in the classroom within the EKF Project lesson for the required version and installation scripts.
Once the install for uWebSocketIO is complete, the main program can be built and run by doing the following from the project top directory.
- mkdir build
- cd build
- cmake ..
- make
- ./ExtendedKF
Tips for setting up your environment can be found in the classroom lesson for this project.
Note that the programs that need to be written to accomplish the project are src/FusionEKF.cpp, src/FusionEKF.h, kalman_filter.cpp, kalman_filter.h, tools.cpp, and tools.h
The program main.cpp has already been filled out, but feel free to modify it.
Here is the main protocol that main.cpp uses for uWebSocketIO in communicating with the simulator.
INPUT: values provided by the simulator to the c++ program
["sensor_measurement"] => the measurement that the simulator observed (either lidar or radar)
OUTPUT: values provided by the c++ program to the simulator
["estimate_x"] <= kalman filter estimated position x ["estimate_y"] <= kalman filter estimated position y ["rmse_x"] ["rmse_y"] ["rmse_vx"] ["rmse_vy"]
- cmake >= 3.5
- All OSes: click here for installation instructions
- make >= 4.1 (Linux, Mac), 3.81 (Windows)
- Linux: make is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: install Xcode command line tools to get make
- Windows: Click here for installation instructions
- gcc/g++ >= 5.4
- Linux: gcc / g++ is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: same deal as make - install Xcode command line tools
- Windows: recommend using MinGW
- Clone this repo.
- Make a build directory:
mkdir build && cd build - Compile:
cmake .. && make- On windows, you may need to run:
cmake .. -G "Unix Makefiles" && make
- On windows, you may need to run:
- Run it:
./ExtendedKF
We've purposefully kept editor configuration files out of this repo in order to keep it as simple and environment agnostic as possible. However, we recommend using the following settings:
- indent using spaces
- set tab width to 2 spaces (keeps the matrices in source code aligned)
Please (do your best to) stick to Google's C++ style guide.
This is optional!
If you'd like to generate your own radar and lidar data, see the utilities repo for Matlab scripts that can generate additional data.
The Project Rubric Points are addressed below -
The code compiles successfully without any errors with cmake and make.
This is shown below through images :
After executing ./ExtendedKF, it ran successfully. First I executed the command, then I opened the simulator and started running the EKF and in the terminal it showed connected as follows :
px, py, vx, vy output coordinates must have an RMSE <= [.11, .11, 0.52, 0.52] when using the file: "obj_pose-laser-radar-synthetic-input.txt" which is the same data file the simulator uses for Dataset 1.
My EKF algorithm ran quite successfully on the Dataset 1 and I got the following accuracy :
RMSE <= [0.0973, 0.0855, 0.4513, 0.4399]
Here is the screenshot of my output :
Your Sensor Fusion algorithm follows the general processing flow as taught in the preceding lessons.
The main Kalman Filter implementation can be found inside the folder src and is named as kalman_filter.cpp.
The predict function has been filled successfully and can be found from lines 25 to 32. The update function for LIDAR has been filled in from lines 34 to 40. The updateEKF function for RADAR is filled in from lines 42 to 65.
To increase the code readability, I made a small function called UpdateWithY from lines 67 to 77 to calculate H_transpose, S_inverse, Kalman gain (K), new state and P as these are used in the update and updateEKF functions. This new function addition has been accounted for inside the kalman_filter.h file as well and I have defined it as private inside the class.
The first measurement has been handled carefully in the file called FusionEKF.cpp from lines 59 to 103 and can be found inside the folder src.
The calling of predict function can be found in the line 141in the file FusionEKF.cpp and the update mechanism has been implemented in the lines 153 to 165. So, it is concluded easily that my KF first predicts then it updates.
In the FusionEKF.cpp file –
The measurement for LIDAR and RADAR is been implemented in the lines 59 to 103, where the first measurement has also been taken care of. Here conditional statements are used for detecting RADAR or LIDAR and then appropriate calculations have been implemented.
The update has been implemented in lines 153 to 165, both for RADAR and LIDAR. Here also conditional statements have been used to detect LIDAR or RADAR and then update equations have been calculated.
In the FusionEKF.cpp file –
From lines 126 to 140, I have calculated the Q matrix, and I have used proper pre calculated values to compute the matrix. This is very good for code optimization as I did not defined any loop to calculate the matrix, didn’t calculated it repeatedly and avoided using any complex data structures as well.