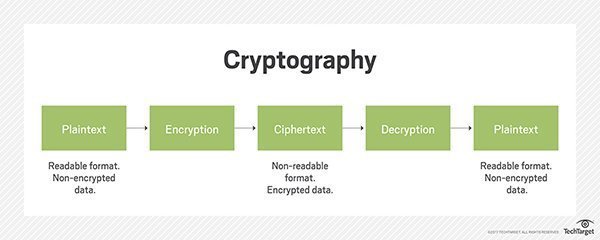
A cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure.
The operation of a cipher usually depends on a piece of auxiliary information, called a key (also known as a cryptovariable). The encrypting procedure is varied depending on the key, which changes the detailed operation of the algorithm. A key must be selected before using a cipher to encrypt a message. Without knowledge of the key, it should be extremely difficult, if not impossible, to decrypt the resulting ciphertext into readable plaintext.
Modern encryption methods can be divided by two criteria: by type of key used, and by type of input data.
By type of key used ciphers are divided into:
symmetric key algorithms (Private-key cryptography), where one same key is used for encryption and decryption
asymmetric key algorithms (Public-key cryptography), where two different keys are used for encryption and decryption.
Ciphers can be distinguished into two types by the type of input data:
block ciphers, which encrypt block of data of fixed size
stream ciphers, which encrypt continuous streams of data.
Symmetric ciphers are most commonly used to secure online communications and are incorporated into many different network protocols to be used to encrypt exchanges. For example, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and TLS use ciphers to encrypt application layer data, especially when used with HTTP Secure (HTTPS).
Virtual private networks (VPNs) that connect remote workers or remote branches into corporate networks use protocols with symmetric ciphers to protect data communications. Symmetric ciphers protect data privacy in most Wi-Fi networks, online banking and e-commerce services, and mobile telephony.
Other protocols, including Secure Shell (SSH), OpenPGP and Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME), use asymmetric cryptography to encrypt and authenticate endpoints but also for the secure exchange of symmetric keys to encrypt session data. While public key cryptography is considered more secure than symmetric encryption, it is also more computationally intensive. For performance reasons, protocols often rely on ciphers to encrypt session data.