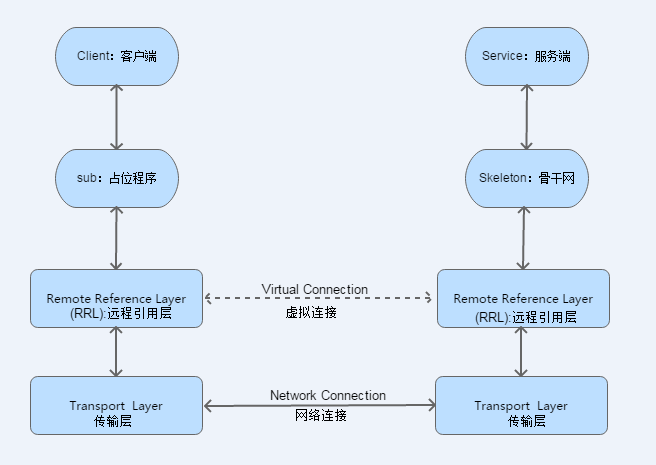
Java RMI,即 远程方法调用(Remote Method Invocation),一种用于实现远程过程调用(RPC)(Remote procedure call)的Java API, 能直接传输序列化后的Java对象和分布式垃圾收集。它的实现依赖于Java虚拟机(JVM),因此它仅支持从一个JVM到另一个JVM的调用。
public class RegistryService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 本地主机上的远程对象注册表Registry的实例,默认端口1099
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
// 创建一个远程对象
HelloRegistryFacade hello = new HelloRegistryFacadeImpl();
// 把远程对象注册到RMI注册服务器上,并命名为HelloRegistry
registry.rebind("HelloRegistry", hello);
System.out.println("======= 启动RMI服务成功! =======");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}继承Remote接口
public interface HelloRegistryFacade extends Remote {
String helloWorld(String name) throws RemoteException;
}
继承UnicastRemoteObject
public class HelloRegistryFacadeImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements HelloRegistryFacade{
public HelloRegistryFacadeImpl() throws RemoteException {
super();
}
@Override
public String helloWorld(String name) {
return "[Registry] 你好! " + name;
}
}
public class RegistryClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(1099);
HelloRegistryFacade hello = (HelloRegistryFacade) registry.lookup("HelloRegistry");
String response = hello.helloWorld("ZhenJin");
System.out.println("=======> " + response + " <=======");
} catch (NotBoundException | RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}出处:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/java_rmi/java_rmi_introduction.htm
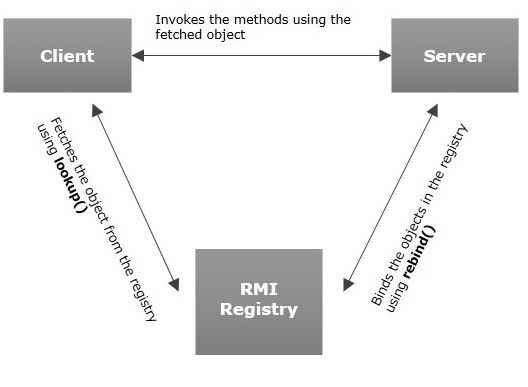
Registry(注册表)是放置所有服务器对象的命名空间。
每次服务端创建一个对象时,它都会使用bind()或rebind()方法注册该对象。
这些是使用称为绑定名称的唯一名称注册的。
要调用远程对象,客户端需要该对象的引用,如(HelloRegistryFacade)。
即通过服务端绑定的名称(HelloRegistry)从注册表中获取对象(lookup()方法)。
public class NamingService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 本地主机上的远程对象注册表Registry的实例
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1100);
// 创建一个远程对象
HelloNamingFacade hello = new HelloNamingFacadeImpl();
// 把远程对象注册到RMI注册服务器上,并命名为Hello
//绑定的URL标准格式为:rmi://host:port/name
Naming.bind("rmi://localhost:1100/HelloNaming", hello);
System.out.println("======= 启动RMI服务成功! =======");
} catch (RemoteException | MalformedURLException | AlreadyBoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}接口和接口实现和Registry的方式一样
public class NamingClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String remoteAddr="rmi://localhost:1100/HelloNaming";
HelloNamingFacade hello = (HelloNamingFacade) Naming.lookup(remoteAddr);
String response = hello.helloWorld("ZhenJin");
System.out.println("=======> " + response + " <=======");
} catch (NotBoundException | RemoteException | MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public static Remote lookup(String name)
throws NotBoundException,java.net.MalformedURLException,RemoteException{
ParsedNamingURL parsed = parseURL(name);
Registry registry = getRegistry(parsed);
if (parsed.name == null)
return registry;
return registry.lookup(parsed.name);
}
Naming其实是对Registry的一个封装
上面说了rmi是通过JVM虚拟机进行一个远程调用的,我们通过Scala,kotlin等jvm语言印证下
object ScalaRmiService extends App {
try {
val user:UserScalaFacade = new UserScalaFacadeImpl
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1103)
Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:1103/UserScala", user)
println("======= 启动RMI服务成功! =======")
} catch {
case e: IOException => println(e)
}
}trait UserScalaFacade extends Remote {
/**
* 通过用户名获取用户信息
*/
@throws(classOf[RemoteException])
def getByName(userName: String): User
/**
* 通过用户性别获取用户信息
*/
@throws(classOf[RemoteException])
def getBySex(userSex: String): List[User]
}
class UserScalaFacadeImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject with UserScalaFacade {
/**
* 模拟一个数据库表
*/
private lazy val userList = List(
new User("Jane", "女", 16),
new User("jack", "男", 17),
new User("ZhenJin", "男", 18)
)
override def getByName(userName: String): User = userList.filter(u => userName.equals(u.userName)).head
override def getBySex(userSex: String): List[User] = userList.filter(u => userSex.equals(u.userSex))
}
实体类必须实现序列化(Serializable)才能进行一个远程传输
class User(name: String, sex: String, age: Int) extends Serializable {
var userName: String = name
var userSex: String = sex
var userAge: Int = age
override def toString = s"User(userName=$userName, userSex=$userSex, userAge=$userAge)"
}
object ScalaRmiClient extends App {
try {
val remoteAddr="rmi://localhost:1103/UserScala"
val userFacade = Naming.lookup(remoteAddr).asInstanceOf[UserScalaFacade]
println(userFacade.getByName("ZhenJin"))
System.out.println("--------------------------------------")
for (user <- userFacade.getBySex("男")) println(user)
} catch {
case e: NotBoundException => println(e)
case e: RemoteException => println(e)
case e: MalformedURLException => println(e)
}
}
public class JavaRmiClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String remoteAddr="rmi://localhost:1103/UserScala";
UserScalaFacade userFacade = (UserScalaFacade) Naming.lookup();
User zhenJin = userFacade.getByName("ZhenJin");
System.out.println(zhenJin);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
List<User> userList = userFacade.getBySex("男");
System.out.println(userList);
} catch (NotBoundException | RemoteException | MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
上面试验可以证明Scala和Java是可以互通的,Scala本身也是可以直接引用Java类的
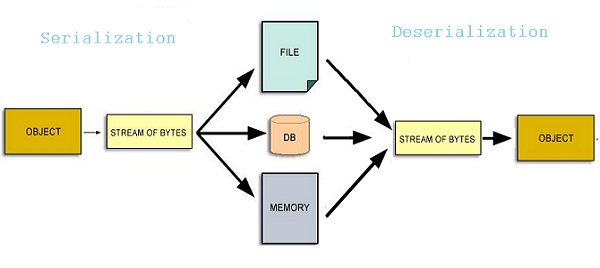
序列化(Serialization)是将数据结构或对象状态转换为可以存储(例如,在文件或存储器缓冲区中)或传输(例如,通过网络连接)的格式的过程, 反序列化(Deserialization)则是从一系列字节中提取数据结构的相反操作.
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
try {
val hello: HelloKotlinFacade = HelloKotlinFacadeImpl()
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1102)
Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:1101/HelloKotlin", hello)
println("======= 启动RMI服务成功! =======")
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}fun main(args: Array<String>) {
try {
val hello = Naming.lookup("rmi://localhost:1102/HelloKotlin") as HelloKotlinFacade
val response = hello.helloWorld("ZhenJin")
println("=======> $response <=======")
} catch (e: NotBoundException) {
e.printStackTrace()
} catch (e: RemoteException) {
e.printStackTrace()
} catch (e: MalformedURLException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}实现和接口省略...
StringBoot通过配置就可以简单实现rmi了
@Configuration
public class RmiServiceConfig {
@Bean
public RmiServiceExporter registerService(UserFacade userFacade) {
RmiServiceExporter rmiServiceExporter = new RmiServiceExporter();
rmiServiceExporter.setServiceName("UserInfo");
rmiServiceExporter.setService(userFacade);
rmiServiceExporter.setServiceInterface(UserFacade.class);
rmiServiceExporter.setRegistryPort(1101);
return rmiServiceExporter;
}
}@Configuration
public class RmiClientConfig {
@Bean
public UserFacade userInfo() {
RmiProxyFactoryBean rmiProxyFactoryBean = new RmiProxyFactoryBean();
rmiProxyFactoryBean.setServiceUrl("rmi://localhost:1101/UserInfo");
rmiProxyFactoryBean.setServiceInterface(UserFacade.class);
rmiProxyFactoryBean.afterPropertiesSet();
return (UserFacade) rmiProxyFactoryBean.getObject();
}
}@Autowired
private UserFacade userFacade;
@Test
public void userBySexTest() {
try {
List<User> userList = userFacade.getBySex("男");
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
通过测试类可以看出,这和我们平时的程序调用内部方法没什么区别!
大家可以通过下面文章加深了解:
-
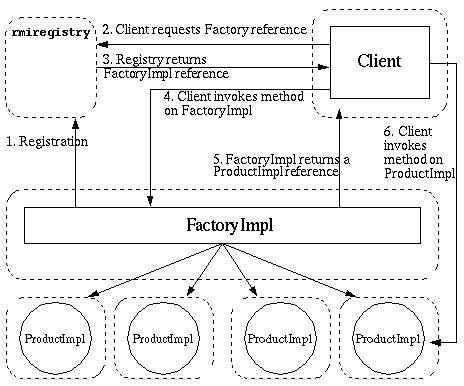
有两个远程服务接口可供client调用,Factory和Product接口
-
FactoryImpl类实现了Factory接口,ProductImpl类实现了Product接口
1. FactoryImpl被注册到了rmi-registry中 2. client端请求一个Factory的引用 3. rmi-registry返回client端一个FactoryImpl的引用 4. client端调用FactoryImpl的远程方法请求一个ProductImpl的远程引用 5. FactoryImpl返回给client端一个ProductImpl引用 6. client通过ProductImpl引用调用远程方法
解压 ZooKeeper
tar -zxvf zookeeper-3.4.12.tar.gz
在 conf 目录新建 zoo.cfg
cd zookeeper-3.4.12/conf
vim zoo.cfg
zoo.cfg 代码如下(自己指定 log 文件目录):
tickTime=2000
dataDir=/usr/local/zookeeper-3.4.12/data
dataLogDir=/usr/local/zookeeper-3.4.12/log
clientPort=2181
在 bin 目录下,启动 Zookeeper:
cd zookeeper-3.4.12/bin
./zkServer.sh start
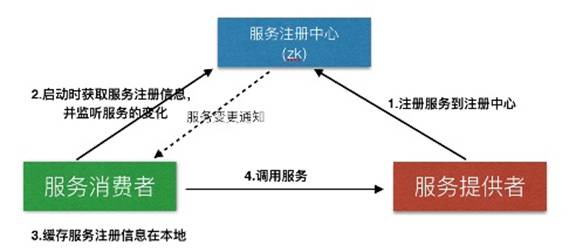
出处:http://www.importnew.com/20344.html
public class RmiConsumer {
// 用于等待 SyncConnected 事件触发后继续执行当前线程
private CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 定义一个 volatile 成员变量,用于保存最新的 RMI 地址(考虑到该变量或许会被其它线程所修改,一旦修改后,该变量的值会影响到所有线程)
private volatile List<String> urlList = new ArrayList<>();
// 构造器
public RmiConsumer() {
ZooKeeper zk = connectServer(); // 连接 ZooKeeper 服务器并获取 ZooKeeper 对象
if (zk != null) {
watchNode(zk); // 观察 /registry 节点的所有子节点并更新 urlList 成员变量
}
}
// 查找 RMI 服务
public <T extends Remote> T lookup() {
T service = null;
int size = urlList.size();
if (size > 0) {
String url;
if (size == 1) {
url = urlList.get(0); // 若 urlList 中只有一个元素,则直接获取该元素
log.debug("using only url: {}", url);
} else {
url = urlList.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(size)); // 若 urlList 中存在多个元素,则随机获取一个元素
log.debug("using random url: {}", url);
}
service = lookupService(url); // 从 JNDI 中查找 RMI 服务
}
return service;
}
// 连接 ZooKeeper 服务器
private ZooKeeper connectServer() {
ZooKeeper zk = null;
try {
zk = new ZooKeeper(Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_STRING, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, new Watcher() {
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
if (event.getState() == Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected) {
latch.countDown(); // 唤醒当前正在执行的线程
}
}
});
latch.await(); // 使当前线程处于等待状态
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
log.error("", e);
}
return zk;
}
// 观察 /registry 节点下所有子节点是否有变化
private void watchNode(final ZooKeeper zk) {
try {
List<String> nodeList = zk.getChildren(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH, event -> {
if (event.getType() == Watcher.Event.EventType.NodeChildrenChanged) {
watchNode(zk); // 若子节点有变化,则重新调用该方法(为了获取最新子节点中的数据)
}
});
List<String> dataList = new ArrayList<>(); // 用于存放 /registry 所有子节点中的数据
for (String node : nodeList) {
byte[] data = zk.getData(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH + "/" + node, false, null); // 获取 /registry 的子节点中的数据
dataList.add(new String(data));
}
log.debug("node data: {}", dataList);
urlList = dataList; // 更新最新的 RMI 地址
} catch (KeeperException | InterruptedException e) {
log.error("", e);
}
}
// 在 JNDI 中查找 RMI 远程服务对象
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> T lookupService(String url) {
T remote = null;
try {
remote = (T) Naming.lookup(url);
} catch (NotBoundException | MalformedURLException | RemoteException e) {
log.error("远程查找出错!", e);
}
return remote;
}
}
public class RmiProvider {
/**
* 用于等待 SyncConnected 事件触发后继续执行当前线程
*/
private CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 发布 RMI 服务并注册 RMI 地址到 ZooKeeper 中
public void publish(Remote remote, String host, int port) {
String url = publishService(remote, host, port); // 发布 RMI 服务并返回 RMI 地址
if (url != null) {
ZooKeeper zk = connectServer(); // 连接 ZooKeeper 服务器并获取 ZooKeeper 对象
if (zk != null) {
createNode(zk, url); // 创建 ZNode 并将 RMI 地址放入 ZNode 上
}
}
}
/**
*发布 RMI 服务
*/
private String publishService(Remote remote, String host, int port) {
String url = null;
try {
url = String.format("rmi://%s:%d/%s", host, port, remote.getClass().getName());
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(port);
Naming.rebind(url, remote);
log.debug("publish rmi service (url: {})", url);
} catch (RemoteException | MalformedURLException e) {
log.error("", e);
}
return url;
}
// 连接 ZooKeeper 服务器
private ZooKeeper connectServer() {
ZooKeeper zk = null;
try {
zk = new ZooKeeper(Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_STRING, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, new Watcher() {
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
if (event.getState() == Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected) {
latch.countDown(); // 唤醒当前正在执行的线程
}
}
});
latch.await(); // 使当前线程处于等待状态
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
log.error("", e);
}
return zk;
}
/**
* 创建节点
*/
private void createNode(ZooKeeper zk, String url) {
try {
byte[] data = url.getBytes();
String path = zk.create(Constant.ZK_PROVIDER_PATH, data, ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL); // 创建一个临时性且有序的 ZNode
log.debug("create zookeeper node ({} => {})", path, url);
} catch (KeeperException | InterruptedException e) {
log.error("", e);
}
}
}
代码已上传到GitHub上:https://github.com/jayknoxqu/rmi-example