PID stands for Proportional-Integral-Derivative. These three controllers are combined in such a way that it produces a control signal. This is how the vehicle uses steering, throttle, and brake to move through the world, executing a trajectory created by the path planning block.
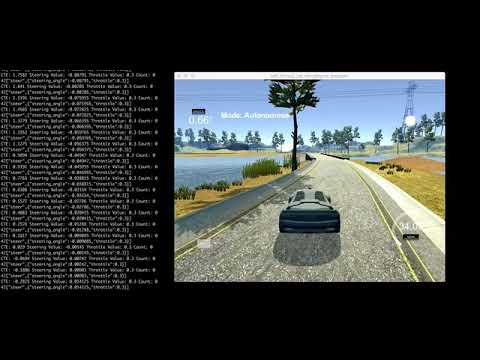
In this project we will revisit the lake race track from the Behavioral Cloning Project. This time, however, we will implement a PID controller in C++ to maneuver the vehicle around the track! The simulator will provide the cross track error (CTE) and the velocity (mph) in order to compute the appropriate steering angle.
I am going to discuss based on how to use PID for steering angles.
A cross track error is a distance of the vehicle from trajectory. In theory it’s best suited to control the car by steering in proportion to Cross Track Error(CTE).
It sets the steering angle in proportion to CTE with a proportional factor tau.
-tau * cte
In other words, the P, or "proportional", component had the most directly observable effect on the car’s behavior. It causes the car to steer proportional (and opposite) to the car’s distance from the lane center(CTE) - if the car is far to the right it steers hard to the left, if it’s slightly to the left it steers slightly to the right.
It’s the differential component of the controller which helps to take temporal derivative of error. This means when the car turned enough to reduce the error, it will help not to overshoot through the x axis.
In other words, the D, or "differential", component counteracts the P component’s tendency to ring and overshoot the center line. A properly tuned D parameter will cause the car to approach the center line smoothly without ringing.
diff_cte = cte - prev_cte
prev_cte = cte
- tau_d * diff_cte
It’s the integral or sum of error to deal with systematic biases.
In other words, the I, or "integral", component counteracts a bias in the CTE which prevents the P-D controller from reaching the center line. This bias can take several forms, such as a steering drift , but I believe that in this particular implementation the I component particularly serves to reduce the CTE around curves.
int_cte += cte
tau_i * int_cte
And combination of these we can get PID controller to control the steering value.
cte = robot.y
diff_cte = cte - prev_cte
prev_cte = cte
int_cte += cte
steer = -tau_p * cte - tau_d * diff_cte - tau_i * int_cte
Parameter optimisation can be done manually or using Twiddle algorithm.
Pseudocode for implementing the Twiddle algorithm is as follows:
function(tol=0.2) {
p = [0, 0, 0]
dp = [1, 1, 1]
best_error = move_robot()
loop untill sum(dp) > tol
loop until the length of p using i
p[i] += dp[i]
error = move_robot()
if err < best_err
best_err = err
dp[i] *= 1.1
else
p[i] -= 2 * dp[i]
error = move_robot()
if err < best_err
best_err = err
dp[i] *= 1.1
else
p[i] += dp[i]
dp[i] *= 0.9
return p
}
The P, or "proportional", component had the most directly observable effect on the car’s behavior. It causes the car to steer proportional (and opposite) to the car’s distance from the lane center(CTE) - if the car is far to the right it steers hard to the left, if it’s slightly to the left it steers slightly to the right.
I got the P value with oscillating behaviour when I set the value to 0.05 and I and D set to zero
Here is the video with P value set to above:
The D, or "differential", component counteracts the P component’s tendency to ring and overshoot the center line. A properly tuned D parameter will cause the car to approach the center line smoothly without ringing.
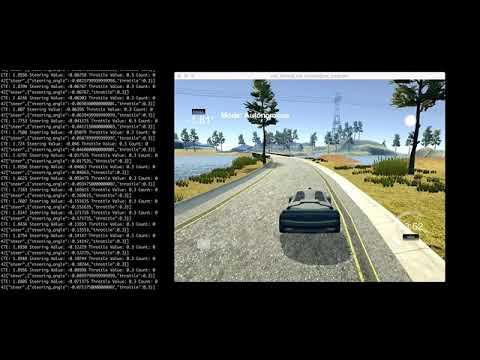
Then found the D value that stops the oscillating behaviour which is set to 1.5 alogn with 0.05 for P and zero for I.
Here is the video after value for P and D as above:
The I, or "integral", component counteracts a bias in the CTE which prevents the P-D controller from reaching the center line. This bias can take several forms, such as a steering drift , but I believe that in this particular implementation the I component particularly serves to reduce the CTE around curves.
In the case of the simulator, no bias is present. We set value to zero.
The intial value for Kp, Ki, Kd selected using trail and error method. It is a simple method of PID controller tuning. In this method, first we have to set Ki and Kd values to zero and increase proportional term (Kp) until system reaches to oscillating behavior. Then Kd was tuned to reduced oscillation and then Ki to reduce steady-state error
And I got the coeffients as below:
{0.05, 0.0001, 1.5}
Then I decided to use Twiddle to optimise these coefficents further. I modified the main.cpp to implement Twiddle algorithm. When twiddle variable set to true, simulator runs the car with confidents till the maximum steps set initially and go through the twiddle algorithm. After competition of each iteration, simulator reset to initial stage and car runs starts from the beginning to maximum steps. This process continuous until tol value below the allowed value.
Finally we got the optimised coeffients as below:
0.06, 0.00031, 1.29