The pivottabler package enables pivot tables to be created with just a few lines of R.
The pivottabler package aims to:
- Provide an easy way of creating pivot tables, without requiring the user to specify low-level layout logic.
- Provide multiple ways of specifying calculation logic to cover both simple and more sophisticated requirements.
- Provide styling options so the pivot tables can be themed/branded as needed.
All calculations for the pivot tables take place inside R, enabling the use of a wide-range of R functions in the calculation logic.
Pivot tables are rendered as htmlwidgets, Latex or plain text. The HTML/Latex/text can be exported for use outside of R.
Pivot tables can be converted to a standard R matrix or data frame. Pivot tables can also be exported to Excel.
pivottabler is a companion package to the basictabler package. pivottabler is focussed on generating pivot tables and can aggregate data. basictabler does not aggregate data but offers more control of table structure.
You can install:
- the latest released version from CRAN with
install.packages("pivottabler")- the latest development version from github with
devtools::install_github("cbailiss/pivottabler", build_vignettes = TRUE)pivottabler has many styling and formatting capabilities when rendering pivot tables in HTML / as htmlwidgets using pt$renderPivot(), however the most basic output is simply as plain text.
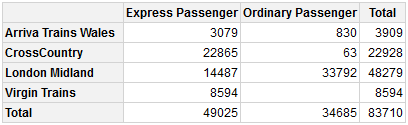
A simple example of creating a pivot table - summarising the types of trains run by different train companies:
library(pivottabler)
# arguments: qpvt(dataFrame, rows, columns, calculations, ...)
qpvt(bhmtrains, "TOC", "TrainCategory", "n()") # TOC = Train Operating Company Express Passenger Ordinary Passenger Total
Arriva Trains Wales 3079 830 3909
CrossCountry 22865 63 22928
London Midland 14487 33792 48279
Virgin Trains 8594 8594
Total 49025 34685 83710
pivottabler also offers a more verbose syntax that is more self-describing and offers additional options that aren't available with the quick-pivot functions. The equivalent verbose commands to output the same pivot table as above are:
library(pivottabler)
pt <- PivotTable$new()
pt$addData(bhmtrains) # bhmtrains is a data frame with columns TrainCategory, TOC, etc.
pt$addColumnDataGroups("TrainCategory") # e.g. Express Passenger
pt$addRowDataGroups("TOC") # TOC = Train Operating Company e.g. Arriva Trains Wales
pt$defineCalculation(calculationName="TotalTrains", summariseExpression="n()")
pt$evaluatePivot()
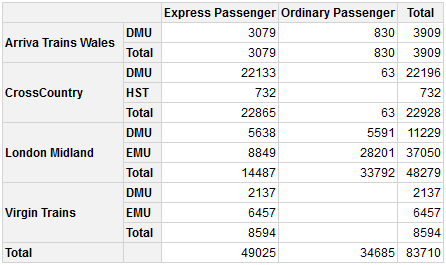
ptMultiple levels can be added to the pivot table row or column headings, e.g. looking at combinations of TOC and PowerType:
library(pivottabler)
qpvt(bhmtrains, c("TOC", "PowerType"), "TrainCategory", "n()")library(pivottabler)
pt <- PivotTable$new()
pt$addData(bhmtrains)
pt$addColumnDataGroups("TrainCategory")
pt$addRowDataGroups("TOC")
pt$addRowDataGroups("PowerType") # D/EMU = Diesel/Electric Multiple Unit, HST=High Speed Train
pt$defineCalculation(calculationName="TotalTrains", summariseExpression="n()")
pt$evaluatePivot()
pt Express Passenger Ordinary Passenger Total
Arriva Trains Wales DMU 3079 830 3909
Total 3079 830 3909
CrossCountry DMU 22133 63 22196
HST 732 732
Total 22865 63 22928
London Midland DMU 5638 5591 11229
EMU 8849 28201 37050
Total 14487 33792 48279
Virgin Trains DMU 2137 2137
EMU 6457 6457
Total 8594 8594
Total 49025 34685 83710
The HTML rendering of the same two pivot tables shown above (each constructed using both a quick-pivot function and verbose syntax) is:
library(pivottabler)
qhpvt(bhmtrains, "TOC", "TrainCategory", "n()") library(pivottabler)
pt <- PivotTable$new()
pt$addData(bhmtrains)
pt$addColumnDataGroups("TrainCategory")
pt$addRowDataGroups("TOC")
pt$defineCalculation(calculationName="TotalTrains", summariseExpression="n()")
pt$renderPivot()library(pivottabler)
qhpvt(bhmtrains, c("TOC", "PowerType"), "TrainCategory", "n()") library(pivottabler)
pt <- PivotTable$new()
pt$addData(bhmtrains) # bhmtrains is a data frame with columns TrainCategory, TOC, etc.
pt$addColumnDataGroups("TrainCategory") # e.g. Express Passenger
pt$addRowDataGroups("TOC") # TOC = Train Operating Company e.g. Arriva Trains Wales
pt$addRowDataGroups("PowerType") # D/EMU = Diesel/Electric Multiple Unit, HST=High Speed Train
pt$defineCalculation(calculationName="TotalTrains", summariseExpression="n()")
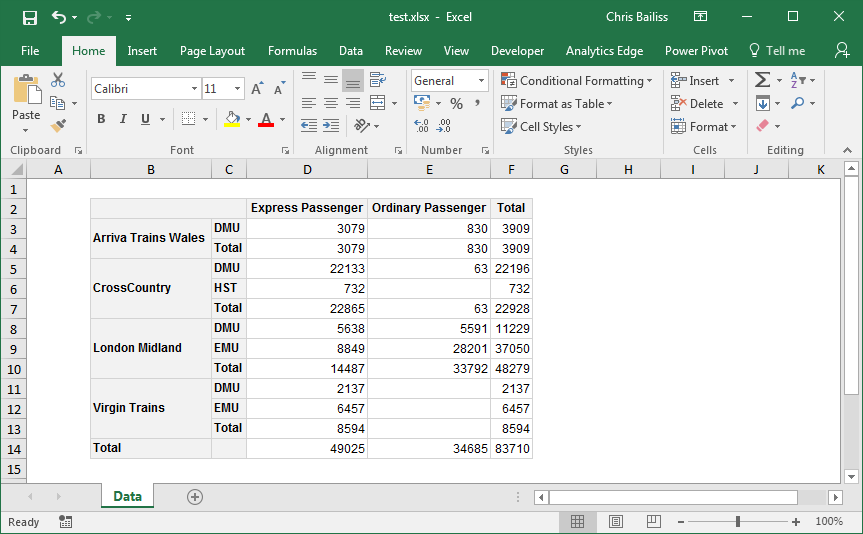
pt$renderPivot()The same styling/formatting used for the HTML output is also used when outputting to Excel - greatly reducing the amount of script that needs to be written to create Excel output.
library(pivottabler)
pt <- PivotTable$new()
pt$addData(bhmtrains) # bhmtrains is a data frame with columns TrainCategory, TOC, etc.
pt$addColumnDataGroups("TrainCategory") # e.g. Express Passenger
pt$addRowDataGroups("TOC") # TOC = Train Operating Company e.g. Arriva Trains Wales
pt$addRowDataGroups("PowerType") # D/EMU = Diesel/Electric Multiple Unit, HST=High Speed Train
pt$defineCalculation(calculationName="TotalTrains", summariseExpression="n()")
pt$evaluatePivot()
library(openxlsx)
wb <- createWorkbook(creator = Sys.getenv("USERNAME"))
addWorksheet(wb, "Data")
pt$writeToExcelWorksheet(wb=wb, wsName="Data",
topRowNumber=2, leftMostColumnNumber=2, applyStyles=TRUE)
saveWorkbook(wb, file="C:\\test.xlsx", overwrite = TRUE)In the screenshot above, Gridlines have been made invisible to make the styling easier to see (by clearing the checkbox on the 'View' ribbon). Columns were also auto-sized - though the widths of columns could also be manually specified from R. See the Excel Export vignette for more details.
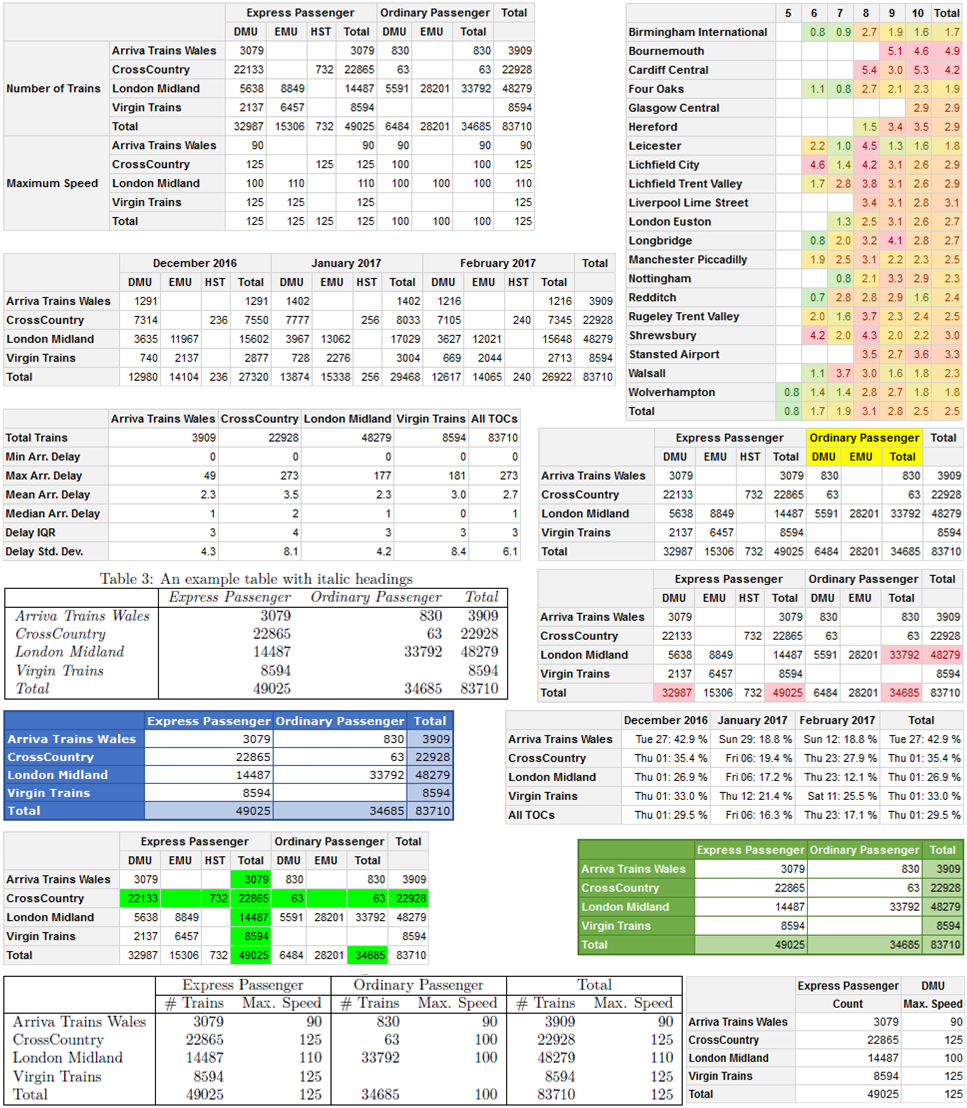
More complex pivot tables can also be created, e.g. with irregular layouts, using multiple data frames, using multiple calculations and/or custom R calculation functions. See the package vignettes for more details:
# to see a list of available package vignettes:
vignette(package="pivottabler")
# to open a specific vignette
vignette(topic="v01-introduction", package="pivottabler")The vignettes can also be read on CRAN at: https://cran.r-project.org/package=pivottabler
The following are a few of the example pivot tables constructed in the package vignettes (click to open full sized picture):