##TOC
- 背景
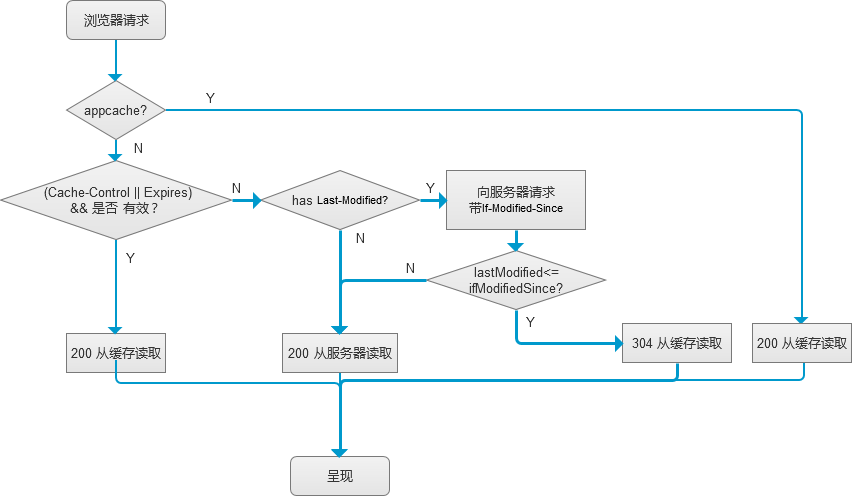
- 浏览器的总流程图
- 一步一步说缓存
- 朴素的静态服务器
- 设置缓存超时时间
- html5 Application Cache
- Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since
- Etag/If-None-Match
- 什么是Etag
- 为什么有了Last-Modified还要Etag
- Etag 的实现
- 迷之浏览器
- 总结
##背景
在对页面的性能优化时,特别是移动端的优化,缓存是非常重要的一环。
浏览器缓存机制设置众多:html5 appcache,Expires,Cache-control,Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since,Etag/If-None-Match,max-age=0/no-cache...,
之前对某一个或几个特性了解一二,但是混在一起再加上浏览器的行为,就迷(meng)糊(bi)了.
下面从实现一个简单的静态服务器角度,一步一步说浏览器的缓存策略。
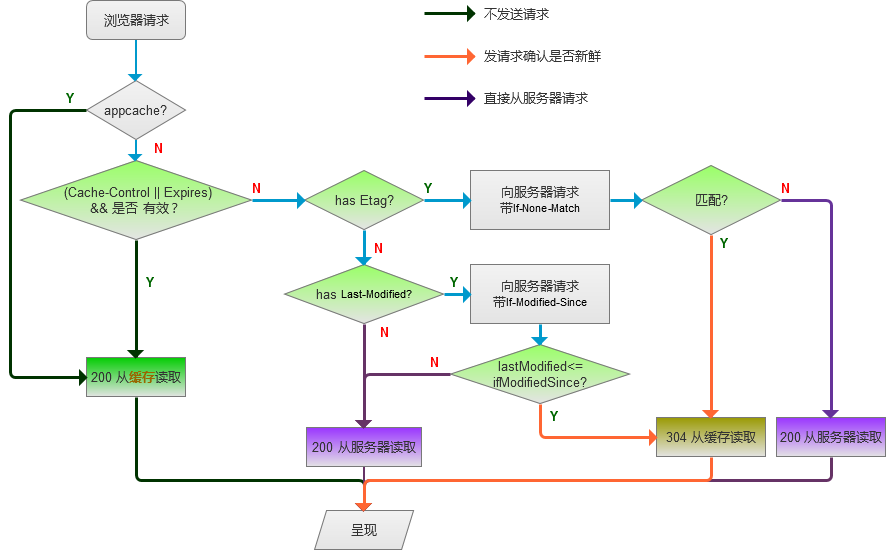
对http请求来说,客户端缓存分三类:
- 不发任何请求,直接从缓存中取数据,代表的特性有: Expires ,Cache-Control=<number!=0>和appcache
- 发请求确认是否新鲜,再决定是否返回304并从缓存中取数据 :代表的特性有:Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since,Etag/If-None-Match
- 直接发送请求, 没有缓存,代表的特性有:Cache-Control:max-age=0/no-cache
时间宝贵,以下是最终的流程图:
源码和流程图源文件在github
浏览的缓存的依据是server http response header , 为了实现对http response 的完全控制,用nodejs实现了一个简单的static 服务器,得益于nodejs简单高效的api,
不到60行就把一个可用的版本实现了:源码
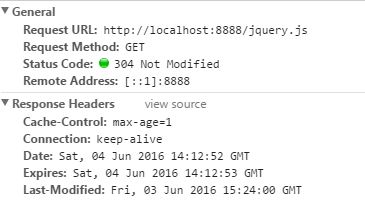
可克隆代码,分支切换到step1, 进入根目录,执行 node app.js,浏览器里输入:http://localhost:8888/index.html,查看response header,返回正常,也没有用任何缓存。
服务器每次都要调用fs.readFile方法去读取硬盘上的文件的。当服务器的请求量一上涨,硬盘IO会成为性能瓶颈(设置了内存缓存除外)。
response header:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html
Date: Fri, 03 Jun 2016 14:15:35 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
对于指定后缀文件和过期日期,为了保证可配置。建立一个config.js。
exports.Expires = {
fileMatch: /^(gif|png|jpg|js|css|html)$/ig,
maxAge: 60*60*24*365
};为了把缓存这个职责独立出来,我们再新建一个cache.js,作为一个中间件处理request.
加上超期时间,代码如下
module.exports = function (request, response) {
var pathname = url.parse(request.url).pathname;
var ext = path.extname(pathname);
ext = ext ? ext.slice(1) : 'unknown';
if (ext.match(config.Expires.fileMatch)) {
var expires = new Date();
expires.setTime(expires.getTime() + config.Expires.maxAge * 1000);
response.setHeader("Expires", expires.toUTCString());
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "max-age=" + config.Expires.maxAge);
}
}这时我们刷新页面可以看到response header 变为这样了:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Expires: Sat, 03 Jun 2017 15:07:23 GMT
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000
Content-Type: text/html
Date: Fri, 03 Jun 2016 15:07:23 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
多了expires,但这是第一次访问,流程和上面一样,还是需要从硬盘读文件,再response
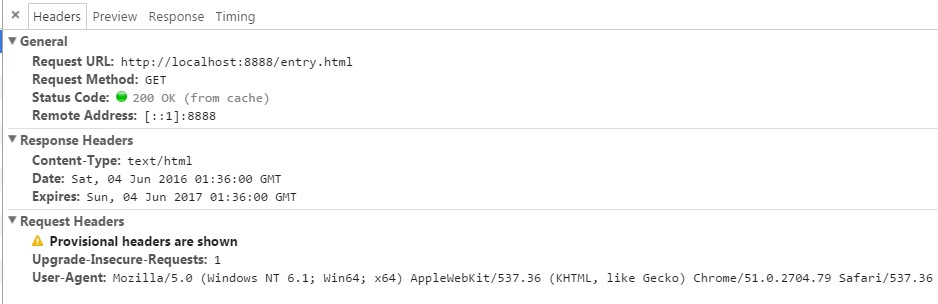
再刷新页面,可以看到http header :
Request URL:http://127.0.0.1:8888/index.html
Request Method:GET
Status Code:200 OK (from cache)
Remote Address:127.0.0.1:8888
但是到这里遇到一个问题,并没有达到预期的效果,并没有从缓存读取
缓存并没有生效。
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:8888
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/50.0.2661.102 Safari/537.36
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, sdch
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8
查看request header 发现 Cache-Control: max-age=0,浏览器强制不用缓存。
浏览器会针对的用户不同行为采用不同的缓存策略:
Chrome does something quite different: 'Cache-Control' is always set to 'max-age=0′, no matter if you press enter, f5 or ctrl+f5. Except if you start Chrome and enter the url and press enter. 其它的浏览器特性可以查看文末的【迷之浏览器】
所以添加文件entry.html,通过链接跳转的方式进入就可以看到cache的效果了。
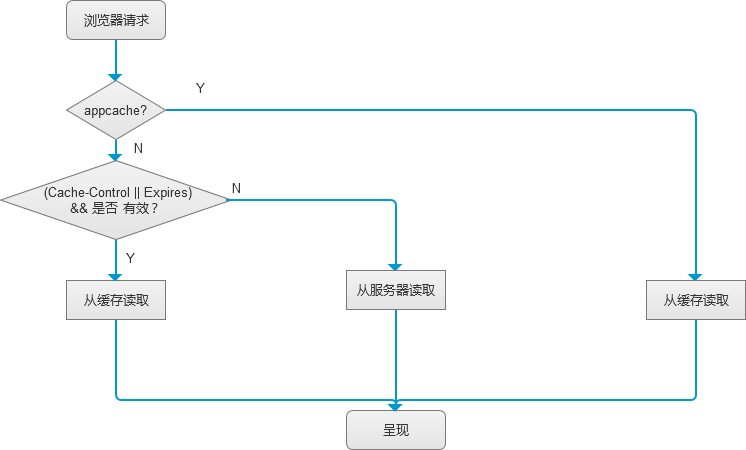
浏览器在发送请求之前由于检测到Cache-Control和Expires(Cache-Control的优先级高于Expires,但有的浏览器不支持Cache-Control,这时采用Expires), 如果没有过期,则不会发送请求,而直接从缓存中读取文件。
Cache-Control与Expires的作用一致,都是指明当前资源的有效期,控制浏览器是否直接从浏览器缓存取数据还是重新发请求到服务器取数据。 只不过Cache-Control的选择更多,设置更细致,如果同时设置的话,其优先级高于Expires。
代码详细可查看源码:https://github.com/etoah/BrowserCachePolicy/tree/step2
除了Expires 和Cache-Control 两个特性的缓存可以让browser完全不发请求的话,别忘了还有一个html5的新特性 Application Cache,
在我的另一篇文章中有简单的介绍HTML5 Application cache初探和企业应用启示.
同时在自己写的代码编辑器中,也用到了此特性,可离线查看,坑也比较多。
为了消除 expires cache-control 的影响,先注释掉这两行,并消除浏览器的缓存。
// response.setHeader("Expires", expires.toUTCString());
//response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "max-age=" + config.Expires.maxAge);新增文件app.manifest,由于appcache 会缓存当前文件,我们可不指定缓存文件,只需输入CACHE MANIFEST,并在entry.html引用这个文件。
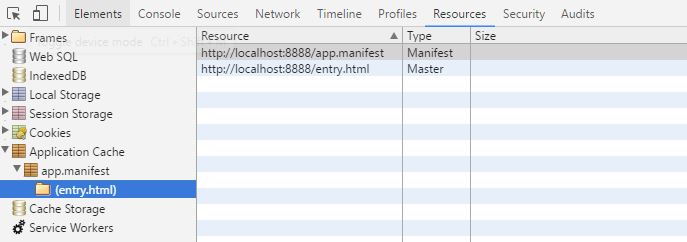
<html lang="en" manifest="app.manifest">在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8888/entry.html,可以看到appcache ,已经在缓存文件了:
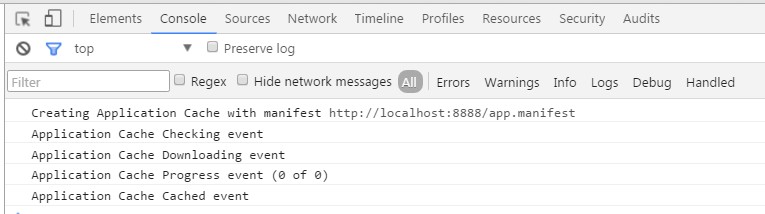
这时再刷新浏览器,可以看到即使没有 Expires 和Cache-Control 也是 from cache ,
而index.html 由于没有加Expires ,Cache-Control和appcache 还是直接从服务器端取文件。
这时缓存的控制如下
本例子的源码为分支 step3:代码详细可查看源码
Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since。
- Last-Modified:标示这个响应资源的最后修改时间。web服务器在响应请求时,告诉浏览器资源的最后修改时间。
- If-Modified-Since:当资源过期时(使用Cache-Control标识的max-age),发现资源具有Last-Modified声明,则再次向web服务器请求时带上头 If-Modified-Since,表示请求时间。web服务器收到请求后发现有头If-Modified-Since 则与被请求资源的最后修改时间进行比对。若最后修改时间较新,说明资源又被改动过,则响应整片资源内容(写在响应消息包体内),HTTP 200;若最后修改时间较旧,说明资源无新修改,则响应HTTP 304 (无需包体,节省浏览),告知浏览器继续使用所保存的cache。
所以我们需要把 Cache-Control 设置的尽可能的短,让资源过期:
exports.Expires = {
fileMatch: /^(gif|png|jpg|js|css|html)$/ig,
maxAge: 1
};同时需要识别出文件的最后修改时间,并返回给客户端,我们同时也要检测浏览器是否发送了If-Modified-Since请求头。如果发送而且跟文件的修改时间相同的话,我们返回304状态。 代码如下:
fs.stat(realPath, function (err, stat) {
var lastModified = stat.mtime.toUTCString();
var ifModifiedSince = "If-Modified-Since".toLowerCase();
response.setHeader("Last-Modified", lastModified);
if (request.headers[ifModifiedSince] && lastModified == request.headers[ifModifiedSince]) {
response.writeHead(304, "Not Modified");
response.end();
}
})如果没有发送或者跟磁盘上的文件修改时间不相符合,则发送回磁盘上的最新文件。
同样我们清缓存,刷新两次就能看到效果如下:
服务器请求确认了文件是否新鲜,直接返回header, 网络负载特别较小:
这时我们的缓存控制流程图如下:
本例子的源码为分支 step4:代码详细可查看源码:https://github.com/etoah/BrowserCachePolicy/tree/step4
除了有Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since组合,还有Etag/if-None-Match,
ETag ,全称Entity Tag.
- Etag:web服务器响应请求时,告诉浏览器当前资源在服务器的唯一标识(生成规则由服务器决定,具体下文中介绍)。
- If-None-Match:当资源过期时(使用Cache-Control标识的max-age),发现资源具有Etage声明,则再次向web服务器请求时带上头If-None-Match (Etag的值)。 web服务器收到请求后发现有头If-None-Match 则与被请求资源的相应校验串进行比对,决定返回200或304。
你可能会觉得使用Last-Modified已经足以让浏览器知道本地的缓存副本是否足够新,为什么还需要Etag(实体标识)呢?HTTP1.1中Etag的出现主要是为了解决几个Last-Modified比较难解决的问题:
- Last-Modified标注的最后修改只能精确到秒级,如果某些文件在1秒钟以内,被修改多次的话,它将不能准确标注文件的修改时间
- 如果某些文件会被定期生成,当有时内容并没有任何变化,但Last-Modified却改变了,导致文件没法使用缓存
- 有可能存在服务器没有准确获取文件修改时间,或者与代理服务器时间不一致等情形
在node 的后端框架express 中引用的是npm包etag,etag 支持根据传入的参数支持两种etag的方式: 一种是文件状态(大小,修改时间),另一种是文件内容的哈希值。 详情可相看etag源码
由上面的目的,也很容易想到怎么简单实现,这里我们对文件内容哈希得到Etag值。
哈希会用到node 中的Crypto模块 ,先引用var crypto = require('crypto');,并在响应时加上Etag:
var hash = crypto.createHash('md5').update(file).digest('base64');
response.setHeader("Etag", hash);
if (
(request.headers['if-none-match'] && request.headers['if-none-match'] === hash)
// ||
// (request.headers[ifModifiedSince] && new Date(lastModified) <= new Date(request.headers[ifModifiedSince]))
) {
response.writeHead(304, "Not Modified");
response.end();
return;
}为了消除 Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since的影响,测试时可以先注释此 header,这里写的是 strong validator,详细可查看W3C ETag 第二次访问时,正常的返回304,并读取缓存
更改文件,etag发生不匹配,返回200
还有一部份功能特性,由于支持度不广(部份客户端不支持(chrome,firefox,缓存代理服务器)不支持,或主流服务器不支持,如nginx, Appache)没有特别的介绍。 到这里最终主要的浏程图已完毕,最终的流程图:
最终代码可查看源码
每个浏览器对用户行为(F5,Ctrl+F5,地址栏回车等)的处理都不一样,详细请查看Clientside Cache Control 以下摘抄一段:
So I tried this for different browsers. Unfortunately it's specified nowhere what a browser has to send in which situation.
- Internet Explorer 6 and 7 do both send only cache refresh hints on ctrl+F5. On ctrl+F5 they both send the header field 'Cache-Control' set to 'no-cache'.
- Firefox 3 do send the header field 'Cache-Control' with the value 'max-age=0′ if the user press f5. If you press ctrl+f5 Firefox sends the 'Cache-Control' with 'no-cache' (hey it do the same as IE!) and send also a field 'Pragma' which is also set to 'no-cache'.
- Firefox 2 does send the header field 'Cache-Control' with the value 'max-age=0′ if the user press f5. ctrl+f5 does not work.
- Opera/9.62 does send 'Cache-Control' with the value 'max-age=0′ after f5 and ctrl+f5 does not work.
- Safari 3.1.2 behaves like Opera above.
- Chrome does something quite different: 'Cache-Control' is always set to 'max-age=0′, no matter if you press enter, f5 or ctrl+f5. Except if you start Chrome and enter the url and press enter.
这只是一篇原理或是规则性的文章,初看起来比较复杂,但现实应用可能只用到了很少的一部份特性就能达到较好的效果: 我们只需在打包的时候用gulp生成md5戳或时间戳,过期时间设置为10年,更新版本时更新戳,缓存策略简单高效。 关于缓存配置的实战这些问题, 比如,appcache,Expires/Cache-Control 都是不需发任何请求,适用于什么场景,怎么选择? 配置时,不是配置express,配的是nginx,怎么配置 ,下篇《详说浏览器缓存-实战篇》更新。
W3C ETag
rfc2616
What takes precedence: the ETag or Last-Modified HTTP header?