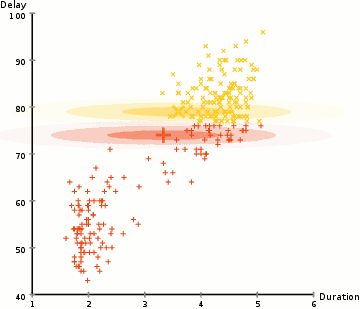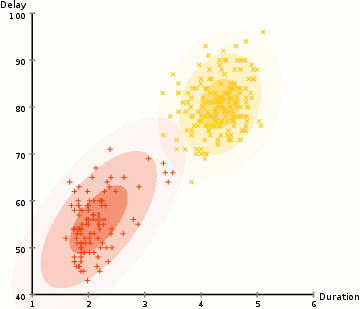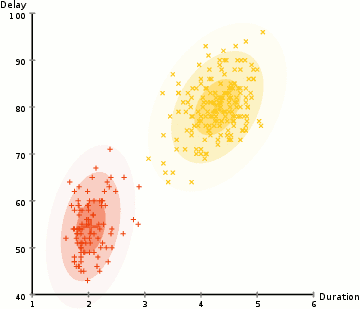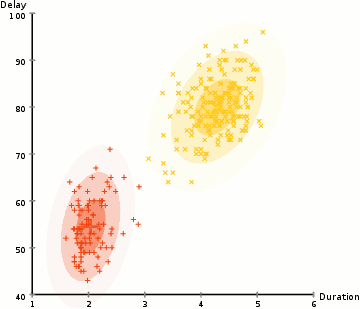
This is part of the IBM Applied Data Science Capstone project.
problem:
finding a new location (location with 30,000 sqft) that our client can put a new location for their new (gym, indoor playyard, trampoline park.) The key is finding a location that is similar to the location that they have has success(60190)
what impacts location?
can we understand trafic flow
housing
income
poverty
parks
forest perserves
roads(big/small)
rail
greenbelt
schools
distance to things of interest?
Haversine distance: distance between points on a sphere given(lat/lon) sin^2(θ/2)
Euclidean distance: ||a-b||2 = √(Σ(ai-bi))
Squared Euclidean distance: ||a-b||22 = Σ((ai-bi)2)
Manhattan distance: ||a-b||1 = Σ|ai-bi|
Maximum distance:||a-b||INFINITY = maxi|ai-bi|
Mahalanobis distance: √((a-b)T S-1 (-b)) {where, s : covariance matrix}
Distance function have an impact so which one should we use?
-
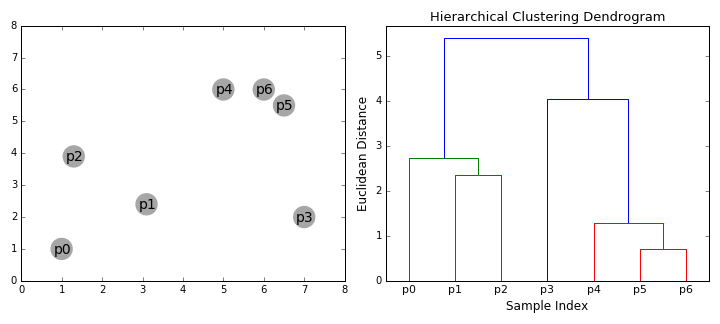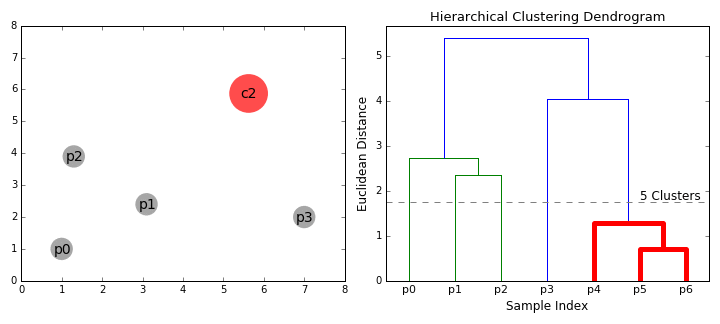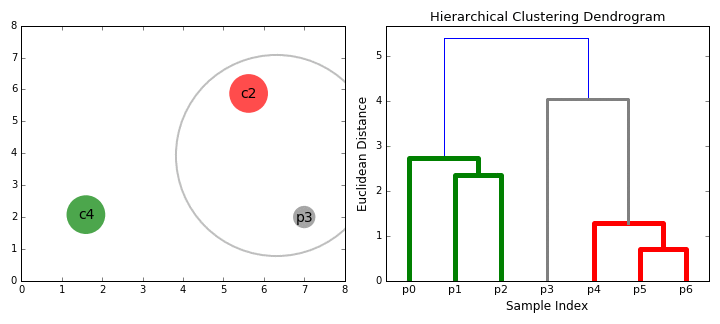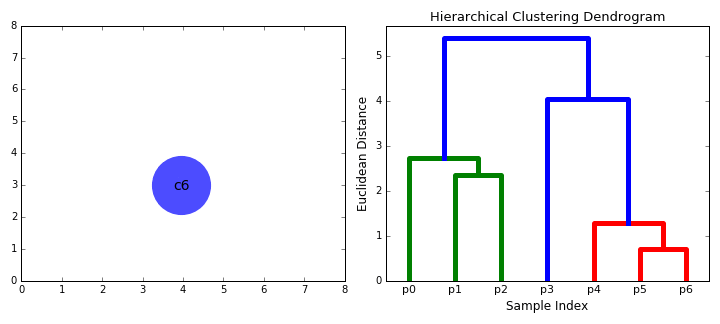
Hierarchical Clustering(more info)
Think about a dendrograms and how the data is seperated into groups
-
Agglomerative:(bottom-up) Each observation starts in its own cluster, and pairs of clusters are merged as we move up the hierarchy.
-
Divisive: (top-down) start with one cluster, then splits are performed recursively down the hierarchy.
Its is an iterative proccess of updating the centroids to find the local optima, so setting the seed could be important for reproducability. You need to define the number of clusters befor hand.
- K-Means
- Kernel K-Means
How probable is it that all data points in the cluster belong to the same distribution (Normal, Gaussian, ect). Downside: Overfitting is a common problem.
- EM(Expectation-maximization) using Gaussian Mixture Models(GMMs) or multivariate normal distributions
assuming we have a Gaussian distributions(normal) we can compute the probability that each data point belongs to a particular cluster, the the higher probability the closer a point is to the clusters center. We then update the set of parameters using a weighed sum to maximize probabilities that the data points are within there given clusters, this proccess can be repeated iteratively until convergence. clusters can take on any ellipse shape. You can have multiple clusters per data point(mixed membership). So if a data point is in the middle of two overlapping clusters(??% class-1 and ??% class-2)
These models search the data space for areas of varied density of data points in the data space. It isolates various different density regions and assign the data points within these regions in the same cluster.
- Mean-Shift Clustering Every iteration the sliding window is shifted towards regions of higher density by shifting the center point to the mean of the points within the window. No need to select the number of cluster, the biggest drawback is the window size/radius “r” can be non-trivial
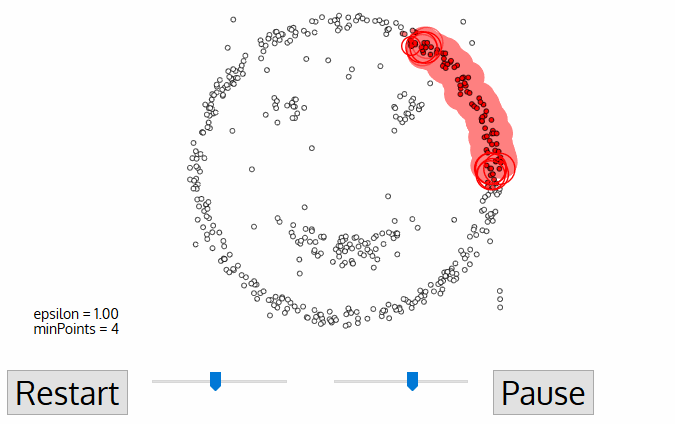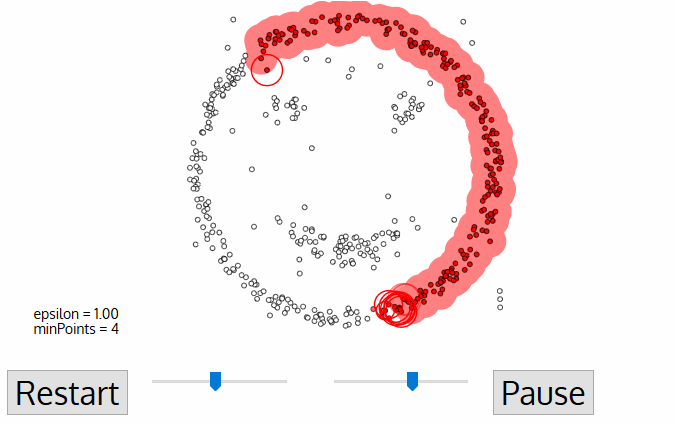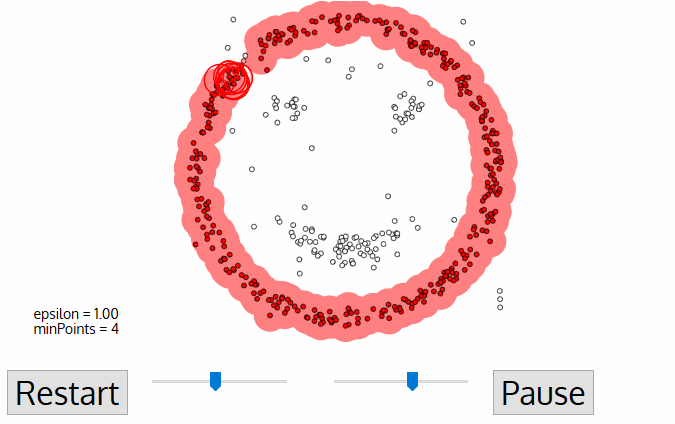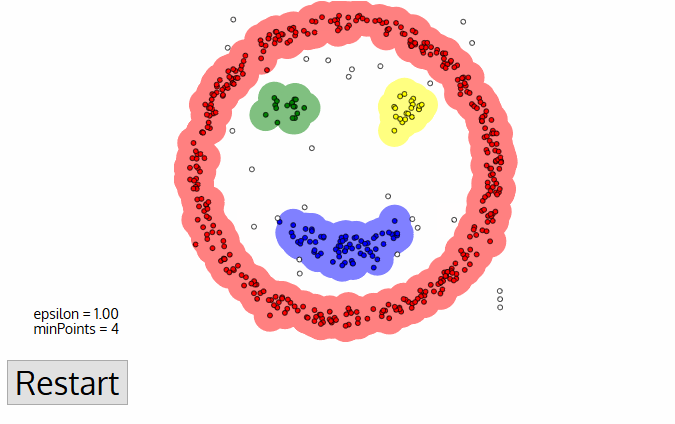
- DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise)
similar to mean-shift. You define the distance(ε-epsilon) that a point would be considered inside a neighborhood (All points which are within the ε distance are neighborhood points), as well as the "minPoints", which is the minimum number of point within the distance(ε) of the current point, otherwise the point is labeled as noise(which later become a cluster). Downside: it doesn’t perform as well as others when the clusters are of varying density
- OPTICS
Testing Clusters
- Silhouette - method of interpretation and validation of consistency within clusters of data.
sources: General
- https://towardsdatascience.com/the-5-clustering-algorithms-data-scientists-need-to-know-a36d136ef68
- https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2016/11/an-introduction-to-clustering-and-different-methods-of-clustering/
- https://stackabuse.com/hierarchical-clustering-with-python-and-scikit-learn/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZVhtchqHlHs
- https://github.com/ardianumam/Machine-Learning-From-The-Scratch/blob/master/kernel_kMeansClustering.py
- https://gist.github.com/mblondel/6230787
Clustering the US population: observation-weighted k-means
- https://towardsdatascience.com/clustering-the-us-population-observation-weighted-k-means-f4d58b370002
- https://github.com/leapingllamas/medium_posts/tree/master/observation_weighted_kmeans
clustering notebooks I liked