This project is not currently being maintained. While I will do my best to help in a timely fashion, you should not expect a prompt response.
The radiomics package is a set of tools for computing texture matrices
and features from images.
The release version of this package (April 2016, v0.1.2) is available from CRAN using:
install.packages("radiomics")Or you can install the development version of the package using:
devtools::install_github("joelcarlson/radiomics")
library(radiomics)In the package are functions for calculating four different types of matrices and associated feature sets used to quantify the texture of an image.
These matrices are the:
- Grey Level Co-occurrence Matrix
- Grey Level Run Length Matrix
- Grey Level Size Zone Matrix
- Multiple Grey Level Size Zone Matrix
Detailed usage directions for calculating features and matrices can be
found in the package vignette (use browseVignettes(package = "radiomics"))
Texture matrices can be created from 2D images by using the abbreviated and lowercase matrix name as a function call:
tumor <- radiomics::tumor #2D MRI slice of a brain tumor
glcm(tumor)
glrlm(tumor)
glszm(tumor)
mglszm(tumor)A matrix with the class of the texture matrix type is returned, as shown
here using glcm(tumor, n_grey=4)
#> An object of class "glcm"
#> 1 2 3 4
#> 1 0.1617021277 0.03356974 0.001891253 0.0004728132
#> 2 0.0335697400 0.38345154 0.010638298 0.0014184397
#> 3 0.0018912530 0.01063830 0.301654846 0.0184397163
#> 4 0.0004728132 0.00141844 0.018439716 0.0203309693
class(glcm(tumor, n_grey=4))[1]
#> [1] "glcm"Each matrix type has an associated image function for visualization of
the results:
image(glcm(tumor))
image(glrlm(tumor))
image(glszm(tumor))
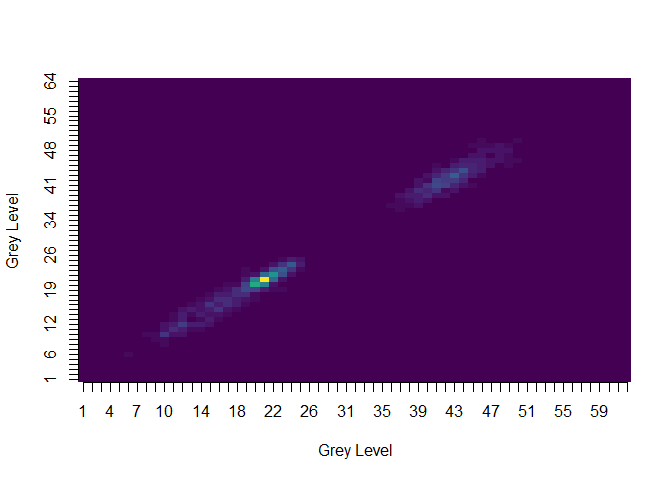
image(mglszm(tumor))The image functions make use of the viridis scale, as shown here
using image(glcm(tumor, n_grey=64)):
Each matrix type has an associated calc_features function, which
returns an object of class data.frame with a single observation for
each calculated feature. First order features can also be calculated on
2D matrices.
calc_features(tumor)
calc_features(glcm(tumor))
calc_features(glrlm(tumor))
calc_features(glszm(tumor))
calc_features(mglszm(tumor))