The Core Bluetooth framework provides the classes needed for your iOS and Mac apps to communicate with devices that are equipped with Bluetooth low energy wireless technology. For example, your app can discover, explore, and interact with low energy peripheral devices, such as heart rate monitors and digital thermostats. As of macOS 10.9 and iOS 6, Mac and iOS devices can also function as Bluetooth low energy peripherals, serving data to other devices, including other Mac and iOS devices. You can find more information in a presentation and video.
Bluetooth low energy wireless technology is based on the Bluetooth 4.0 specification, which, among other things, defines a set of protocols for communicating between low energy devices. The Core Bluetooth framework is an abstraction of the Bluetooth low energy protocol stack. That said, it hides many of the low-level details of the specification from you, the developer, making it much easier for you to develop apps that interact with Bluetooth low energy devices.
The Core Bluetooth framework provides the classes needed for your apps to communicate with Bluetooth-equipped low energy (LE) and Basic Rate / Enhanced Data Rate (BR/EDR) wireless technology.
We need the CBCentralManager object that scans for, discovers, connects to, and manages peripherals. We'll also need the CBPeripheral object that represents remote peripheral devices that your app discovers with a central manager.
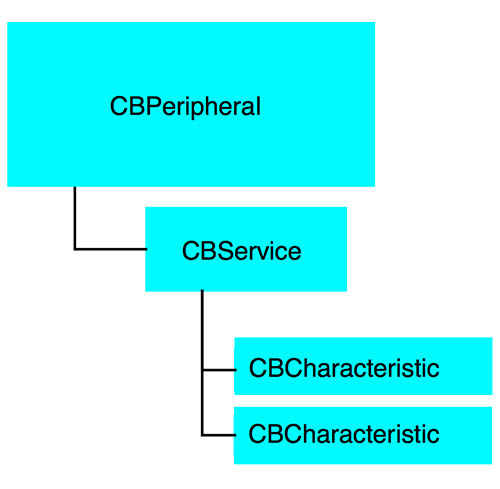
A CBPeripheral is used to discover, explore, and interact with the services available on a remote peripheral that supports Bluetooth low energy.
A service encapsulates the way part of the device behaves. For example, one service of a heart rate monitor may be to expose heart rate data from a sensor.
Services themselves contain of characteristics or included services (references to other services).
Characteristics provide further details about a peripheral’s service. For example, the heart rate service may contain multiple characteristics.
The following diagram shows the hierarchy of the CBPeripheral:
Before starting to code, you need to create a prompt that asks for permission to use the device's Bluetooth.
Add these to your info.plist:
• Privacy - Bluetooth Peripheral Usage Description
• Privacy - Bluetooth Always Usage Description
Now create variable to store your central manager. The central manager manages discovered or connected remote peripheral devices (represented by CBPeripheral objects), including scanning for, discovering, and connecting to advertising peripherals. Then in your viewDidLoad, initialize the central manager by setting the delegate to self, otherwise the central state never changes on startup.
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
centralManager = CBCentralManager(delegate: self, queue: nil)
}This is much easier and simple to read, but the best part comes from the caller's side. When we want to use the result of a function marked as async, we need to make sure that its execution is already completed. To make this possible, we need to write the await keyword in front of the function call. By doing this, the current execution will be paused until the result is available for its use.
let products = await fetchProducts()
for product in products {
let offerText = await getOffer(for: product.id)
if !offerText.isEmpty {
let productOffer = ProductOffer(productId: product.id, offer: offerText)
offers.append(productOffer)
}
}Now add a CBCentralManagerDelegate protocol to the ViewController in order to scan, discover and connect a peripheral. The CBCentralManagerDelegate protocol defines the methods that a delegate of a CBCentralManager object must adopt.
extension ViewController: CBCentralManagerDelegate {
func centralManagerDidUpdateState(_ central: CBCentralManager) {
switch central.state {
case .poweredOff:
print("Is Powered Off.")
case .poweredOn:
print("Is Powered On.")
startScanning()
case .unsupported:
print("Is Unsupported.")
case .unauthorized:
print("Is Unauthorized.")
case .unknown:
print("Unknown")
case .resetting:
print("Resetting")
@unknown default:
print("Error")
}
}
}Scanning for Peripherals Once the CBCentralManager is up and powered on, you can create a function that scan for peripherals around us.
Create a function called startScanning. Call the method scanForPeripherals(withServices:).
This method scans for peripherals that are advertising services. Now since the unique identifier is set up, add that reference to the method.
func startScanning() -> Void {
// Start Scanning
centralManager?.scanForPeripherals(withServices: [CBUUIDs.BLEService_UUID])
}Now add the startScanning() function to the centralManagerDidUpdateState to scan as soon as the app opens.
extension ViewController: CBCentralManagerDelegate {
func centralManagerDidUpdateState(_ central: CBCentralManager) {
switch central.state {
case .poweredOff:
print("Is Powered Off.")
case .poweredOn:
print("Is Powered On.")
startScanning()
case .unsupported:
print("Is Unsupported.")
case .unauthorized:
print("Is Unauthorized.")
case .unknown:
print("Unknown")
case .resetting:
print("Resetting")
@unknown default:
print("Error")
}
}
}Now that scanning is started, what happens when a peripheral is discovered?
Every time a peripheral is discovered, the CBCentralManager will notify you by calling the centralManager(_:didDiscover:advertisementData:rssi:) function on its delegate.
This function provides the following information about the newly discovered peripheral:
- The discovered peripheral is recognized and can be stored as a CBPeripheral.
- The discovered peripheral has stored advertisement data.
- The current received signal strength indicator (RSSI) of the peripheral, in decibels. Since you are interested in connecting to one peripheral, create an instance of a peripheral.
private var bluefruitPeripheral: CBPeripheral!Call the didDiscover function. This tells the delegate the central manager discovered a peripheral while scanning for devices.
func centralManager(_ central: CBCentralManager, didDiscover peripheral: CBPeripheral,advertisementData: [String : Any], rssi RSSI: NSNumber) {
bluefruitPeripheral = peripheral
bluefruitPeripheral.delegate = self
print("Peripheral Discovered: \(peripheral)")
print("Peripheral name: \(peripheral.name)")
print ("Advertisement Data : \(advertisementData)")
centralManager?.stopScan()
}The implementation of this function performs the following actions:
Set the bluefruitPeripheral variable to the new peripheral found. Set the peripheral's delegate to self (ViewController) Printed the newly discovered peripheral's information in the console. Stopped scanning for peripherals. Next up - actually connect to that peripheral.
To connect to a peripheral, use this method to establish a local connection to the desired peripheral.
centralManager?.connect(blePeripheral!, options: nil)Add this to the didDiscover function.
func centralManager(_ central: CBCentralManager, didDiscover peripheral: CBPeripheral,advertisementData: [String : Any], rssi RSSI: NSNumber) {
bluefruitPeripheral = peripheral
bluefruitPeripheral.delegate = self
print("Peripheral Discovered: \(peripheral)")
print("Peripheral name: \(peripheral.name)")
print ("Advertisement Data : \(advertisementData)")
centralManager?.connect(bluefruitPeripheral!, options: nil)
}Now that the peripheral's services are successfully discovered, the central manager will call the didDiscoverServices() delegate function. didDiscoverService() handles and filters services, so that you can use whichever service you are interested in right away.
func peripheral(_ peripheral: CBPeripheral, didDiscoverServices error: Error?) {
print("*******************************************************")
if ((error) != nil) {
print("Error discovering services: \(error!.localizedDescription)")
return
}
guard let services = peripheral.services else {
return
}
//We need to discover the all characteristic
for service in services {
peripheral.discoverCharacteristics(nil, for: service)
}
print("Discovered Services: \(services)")
}At the same time, the following class example of the same article would not have implicit conformance:
// Does not implicitly conform to Sendable
class Article {
var views: Int
}First, handle any possible errors returned by the central manager, then request characteristics for each service returned by calling discoverCharacteristics(_:)
Discovering Characteristics
private var txCharacteristic: CBCharacteristic!
private var rxCharacteristic: CBCharacteristic!Now call the discoverCharacteristics(_:) function, the central manager will call the didDiscoverCharacteristicsFor() delegate function and provide the discovered characteristics of the specified service.
func peripheral(_ peripheral: CBPeripheral, didDiscoverCharacteristicsFor service: CBService, error: Error?) {
guard let characteristics = service.characteristics else {
return
}
print("Found \(characteristics.count) characteristics.")
for characteristic in characteristics {
if characteristic.uuid.isEqual(CBUUIDs.BLE_Characteristic_uuid_Rx) {
rxCharacteristic = characteristic
peripheral.setNotifyValue(true, for: rxCharacteristic!)
peripheral.readValue(for: characteristic)
print("RX Characteristic: \(rxCharacteristic.uuid)")
}
if characteristic.uuid.isEqual(CBUUIDs.BLE_Characteristic_uuid_Tx){
txCharacteristic = characteristic
print("TX Characteristic: \(txCharacteristic.uuid)")
}
}
}A couple of things are happening in this function:
Handle errors and print characteristic info to the debug console Look through the array of characteristics for a match to desired UUIDs. Perform any necessary actions for the matching characteristics Discover descriptors for each characteristic In this case, the specific UUIDs we're looking for are stored in the BLE_Characteristic_uuid_Rx and BLE_Characteristic_uuid_Tx variables.
When it finds the RX characteristic, it subscribe to updates to its value by calling setNotifyValue() - this is how to receive data from the peripheral. Additionally, read the current value from the characteristic and print its information to the console.
When it finds the TX characteristic, it saves a reference to it to write values to it later - this is how to send data to the peripheral.
Since peripheral.setNotifyValue has been called previously in the didDiscoverCharacteristicsFor method, you are able to set notifications or indications for incoming values registered to the rxcharacteristic.
Once receiving incoming values from a Bluetooth device, Core Bluetooth invokes didUpdateValueFor to handle that incoming data.
func peripheral(_ peripheral: CBPeripheral, didUpdateValueFor characteristic: CBCharacteristic, error: Error?) {
var characteristicASCIIValue = NSString()
guard characteristic == rxCharacteristic,
let characteristicValue = characteristic.value,
let ASCIIstring = NSString(data: characteristicValue, encoding: String.Encoding.utf8.rawValue) else { return }
characteristicASCIIValue = ASCIIstring
print("Value Recieved: \((characteristicASCIIValue as String))")
}You've successfully demonstrated the Bluetooth app's functionality and learned the basics of BLE communication using CoreBluetooth.
Build a Bluetooth App using Swift 5
Core Bluetooth Tutorial for iOS: Heart Rate Monitor
- Panteleimenko Anton, CHI Software
- Kosyi Vlad, CHI Software
Copyright 2021 CHI Software.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.