Save everything you need to compare and reproduce models — architecture, hyperparameters, weights, model predictions, GPU usage, git commits, and even datasets — in 5 minutes. W&B is free for personal use and academic projects, and it's easy to get started.
Install wandb library and login:
pip install wandb
wandb login
Flexible integration for any Python script:
import wandb
# 1. Start a W&B run
wandb.init(project='gpt3')
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.learning_rate = 0.01
# Model training code here ...
# 3. Log metrics over time to visualize performance
for i in range (10):
wandb.log({"loss": loss})If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to ask in our Slack community.
Set wandb.config once at the beginning of your script to save your hyperparameters, input settings (like dataset name or model type), and any other independent variables for your experiments. This is useful for analyzing your experiments and reproducing your work in the future. Setting configs also allows you to visualize the relationships between features of your model architecture or data pipeline and the model performance (as seen in the screenshot above).
wandb.init()
wandb.config.epochs = 4
wandb.config.batch_size = 32
wandb.config.learning_rate = 0.001
wandb.config.architecture = "resnet"Use the Keras callback to automatically save all the metrics and the loss values tracked in model.fit. To get you started here's a minimal example.
# Import W&B
import wandb
from wandb.keras import WandbCallback
# Step1: Initialize W&B run
wandb.init(project='project_name')
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.learning_rate = 0.01
# Model training code here ...
# Step 3: Add WandbCallback
model.fit(X_train, y_train, validation_data=(X_test, y_test),
callbacks=[WandbCallback()])W&B provides first class support for PyTorch. To automatically log gradients and store the network topology, you can call watch and pass in your PyTorch model.
import wandb
# 1. Start a new run
wandb.init(project="gpt-3")
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.dropout = 0.01
# 3. Log gradients and model parameters
wandb.watch(model)
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
...
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
# 4. Log metrics to visualize performance
wandb.log({"loss": loss})The simplest way to log metrics in TensorFlow is by logging tf.summary with the TensorFlow logger.
import wandb
# 1. Start a W&B run
wandb.init(project='gpt3')
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.learning_rate = 0.01
# Model training here
# 3. Log metrics over time to visualize performance
with tf.Session() as sess:
# ...
wandb.tensorflow.log(tf.summary.merge_all())You can use wandb to visualize and compare your scikit-learn models' performance with just a few lines of code.
import wandb
wandb.init(project="visualize-sklearn")
# Model training here
# Log classifier visualizations
wandb.sklearn.plot_classifier(clf, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, y_pred, y_probas, labels, model_name='SVC', feature_names=None)
# Log regression visualizations
wandb.sklearn.plot_regressor(reg, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, model_name='Ridge')
# Log clustering visualizations
wandb.sklearn.plot_clusterer(kmeans, X_train, cluster_labels, labels=None, model_name='KMeans')Visualize, compare, and iterate on fastai models using Weights & Biases with the WandbCallback.
import wandb
fastai2.callback.wandb import WandbCallback
# 1. Start a new run
wandb.init(project="gpt-3")
# 2. Automatically log model metrics
learn.fit(..., cbs=WandbCallback())Run a script with the Trainer, which automatically logs losses, evaluation metrics, model topology and gradients
# 1. Install the wandb library
pip install wandb
# 2. Run a script that has the Trainer to automatically logs metrics, model topology and gradients
python run_glue.py \
--model_name_or_path bert-base-uncased \
--task_name MRPC \
--data_dir $GLUE_DIR/$TASK_NAME \
--do_train \
--evaluate_during_training \
--max_seq_length 128 \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 32 \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--output_dir /tmp/$TASK_NAME/ \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--logging_steps 50Use our callback to compare results between different versions of your XGBoost model.
import wandb
# 1. Start a new run
wandb.init(project="visualize-models", name="xgboost")
# 2. Add the callback
bst = xgboost.train(param, xg_train, num_round, watchlist, callbacks=[wandb.xgboost.wandb_callback()])
# Get predictions
pred = bst.predict(xg_test)Use our callback to visualize your LightGBM’s performance in just one line of code.
import wandb
import numpy as np
import xgboost as xgb
# 1. Start a W&B run
wandb.init(project="visualize-models", name="xgboost")
# 2. Add the wandb callback
bst = gbm = lgb.train(params,
lgb_train,
num_boost_round=20,
valid_sets=lgb_eval,
valid_names=('validation'),
callbacks=[wandb.lightgbm.callback()])
# Get prediction
pred = bst.predict(xg_test)Use Weights & Biases Sweeps to automate hyperparameter optimization and explore the space of possible models.
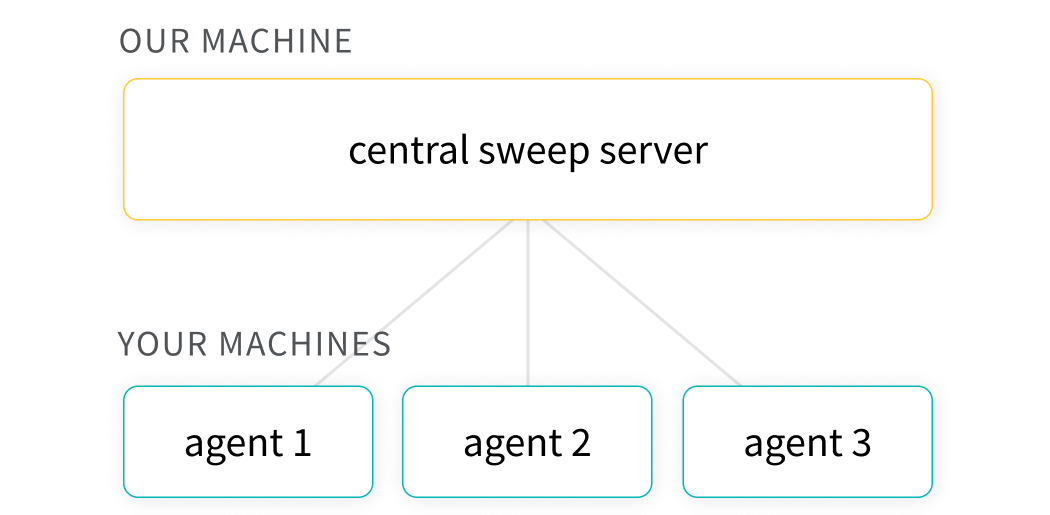
- Quick setup: With just a few lines of code you can run W&B sweeps.
- Transparent: We cite all the algorithms we're using, and our code is open source.
- Powerful: Our sweeps are completely customizable and configurable. You can launch a sweep across dozens of machines, and it's just as easy as starting a sweep on your laptop.
- Explore: Efficiently sample the space of hyperparameter combinations to discover promising regions and build an intuition about your model.
- Optimize: Use sweeps to find a set of hyperparameters with optimal performance.
- K-fold cross validation: Here's a brief code example of k-fold cross validation with W&B Sweeps.
The hyperparameter importance plot surfaces which hyperparameters were the best predictors of, and highly correlated to desirable values for your metrics.
Parallel coordinates plots map hyperparameter values to model metrics. They're useful for honing in on combinations of hyperparameters that led to the best model performance.
Reports let you organize visualizations, describe your findings, and share updates with collaborators.
- Notes: Add a graph with a quick note to yourself.
- Collaboration: Share findings with your colleagues.
- Work log: Track what you've tried, and plan next steps.
Explore reports in The Gallery → | Docs
Once you have experiments in W&B, easily visualize results in reports. Here's a quick overview video.
If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to ask in our Slack community.
We've created some simple examples that show how to use wandb to track experiments with different frameworks. They should be easy to use.
- Install wandb
pip install wandb
- Clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/wandb/examples
- Create a free account (optional)
wandb login
Example deep learning projects that use wandb's features.
Trains a fashion mnist classifier with a small CNN using the keras framework with the tensorflow backend. Uses a simple integration with WandbKerasCallback.
cd examples/keras/keras-cnn-fashion
python train.py
Trains a small CNN on images of plants and animals using Keras. Highly configurable through command line flags: run with -h to see all the options.
The data_tools directory contains a helper script to generate more manageable training datasets from the full 186GB iNaturalist 2017 dataset. A 12K subset of the data can be downloaded by clicking this link. For more context on this example, see this blog post and this W&B report, which explores various settings and hyperparameters.
cd examples/keras/keras-cnn-nature
python train_small_cnn.py
Enables two kinds of finetuning experiments:
- loading various pretrained base CNNs (Xception,ResNet, InceptionResNetV2, InceptionV3), pretraining for some epochs, freezing some of the layers of the resulting network, then continuing to finetune the rest of the layers
- loading a small CNN, pretraining on general labels (in this case, predicting one of 5 biological classes) for a certain number of epochs, then finetuning on specific labels (predicting one of 25 biological species)
Highly configurable with commandline flags: run with -h to see all the options.
cd examples/keras/keras-cnn-nature
python finetune_experiments.py
Trains a GAN on mnist data using a CNN in the keras framework with the tensorflow backend. This shows a more complicated integration with wandb using a custom callback on the generator model and the discriminator model.
cd examples/keras/keras-gan-mnist
python train.py
Trains a fashion mnist classifier with a small CNN using the tensorflow framework.
cd examples/tensorflow/tf-cnn-fashion
python train.py
Trains a fashion mnist classifier with a small CNN using the pytorch framework.
cd examples/pytorch/pytorch-cnn-fashion
python train.py
Trains a 121 layer DenseNet on the Food-101 dataset using the 1cycle learning rate policy, mixed precision training, mixup data augmentation, and progressive resizing.
cd examples/fastai/fastai-food101
pip install -r requirements.txt
python train.py
Trains a semantic segmentation on a dataset from the game "witness"
cd examples/fastai/fastai-unet-segmentation
pip install -r requirements.txt
python train.py
Trains an SVM on the Iris dataset using scikit-learn
cd examples/scikit/scikit-iris
python train.py
Trains a gradient boosted forest on the dermatology dataset
cd examples/boosting-algorithms/xgboost-dermatology
python train.py