swarm-gcp-faas
This project shows how you can create a Docker Swarm cluster on Google Cloud with Terraform, run OpenFaaS on top of Swarm and instrument everything with Weave Cloud Scope and Prometheus.
Install
Clone the repository and install the dependencies:
$ git clone https://github.com/stefanprodan/swarm-gcp-faas.git
$ cd swarm-gcp-faas
$ terraform initBefore running the project you'll have to create a GCP service account key.
Go to Google Cloud Platform -> API Manager -> Credentials -> Create Credentials -> Service account key and
chose JSON as key type. Rename the file to account.json and put it in the project root next to main.tf.
Add your SSH key under Compute Engine -> Metadata -> SSH Keys, also create a metadata entry named sshKeys
with your public SSH key as value.
Docker Swarm bootstrap
Create a Docker Swarm cluster with three managers and three workers:
# create a workspace
terraform workspace new swarm
terraform apply \
-var project=my-swarm-proj \
-var manager_instance_count=3 \
-var manager_machine_type=n1-standard-1 \
-var manager_disk_size=50 \
-var worker_instance_count=3 \
-var worker_machine_type=n1-standard-2 \
-var worker_disk_size=50 \
-var docker_version=17.09.1~ce-0~ubuntu \
-var management_ip_range=35.198.189.7This will do the following:
- creates a dedicated network and a firewall rule to allow internal traffic between swarm nodes
- reserves a public IP for each manager node
- provisions 6 VMs with Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and a 50GB boot disk
- starts the manager nodes and installs Docker CE and the Stackdrive logging agent via SSH
- customizes the Docker daemon systemd config by enabling the experimental features and the metrics endpoint
- initializes the first manager node as the Docker Swarm leader and extracts the join tokens
- starts the worker nodes in parallel and setups Docker CE the same as on the manager node
- joins the worker nodes in the cluster using the manager node private IP
- creates a firewall rule to allow HTTP/S inbound traffic on all nodes
- allows traffic to the Docker remote API only from the IP specified with
management_ip_range
The naming convention for a swarm node is in <WORKSPACE>-<ROLE>-<INDEX> format,
running the project on workspace swarm will create 6 nodes distributed across three zones:
If you don't create a workspace then you'll be running on the default one and your nods prefix will be default.
You can have multiple workspaces, each with it's own state, so you can run in parallel different Docker Swarm clusters.
With these environment variables you can change the region and zones:
TF_VAR_region=us-central1
TF_VAR_zones='["us-central1-b", "us-central1-c", "us-central1-f"]'After applying the Terraform plan you'll see several output variables like the public IPs of each node and the current workspace. You can use the manager public IP variable to connect to the Docker remote API and run docker swarm commands.
$ export DOCKER_HOST=$(terraform output swarm_manager_ip)
$ docker node ls
ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS
4c1wrv1fw78qo81h98ox1soij * swarm-manager-1 Ready Active Leader
4c1wrv1fw78qo81h98ox1soij swarm-manager-2 Ready Active Reachable
axxu7bhhtn96pz7cu1udlhub0 swarm-manager-3 Ready Active Reachable
lqpdwnum0lt8rr0w2u6enudu7 swarm-worker-1 Ready Active
mhjb760b7a11d0fdqi48tdit4 swarm-worker-2 Ready Active
yv27bmn1wfrpy7wuvl603z07i swarm-worker-3 Ready ActiveThe VMs logs are shipped to Stackdrive by the google-fluentd agent. If you want to query Stackdrive for Docker engine demon errors and warnings you can use this filter:
resource.type:"gce_instance"
textPayload:"dockerd"
NOT textPayload:"level=info"You can tear down the whole infrastructure with:
terraform destroy -forceDocker Swarm node scaling
You can scale up or down the Docker Swarm cluster by modifying the worker_instance_count.
On scale up, all new nodes will join the current cluster.
When you scale down the workers, Terraform will first drain the node
and remove it from the swarm before destroying the resources.
# create the cluster with 2 workers
terraform apply \
-var project=my-swarm-proj \
-var worker_instance_count=2
# add one worker
terraform apply \
-var project=my-swarm-proj \
-var worker_instance_count=3
# remove two workers
terraform apply \
-var project=my-swarm-proj \
-var worker_instance_count=1The same scaling operations can be applied to manager nodes using the manager_instance_count variable,
always use an odd number of manager.
# add two managers
terraform apply \
-var project=my-swarm-proj \
-var manager_instance_count=5When removing a manager, Terraform will execute docker swarm leave --force before destroying the resource,
this could break the cluster if there aren't enough managers left to maintain a quorum.
Weave Cloud setup
Now that you have a Docker Swarm cluster up and running you can start monitoring it with Weave Cloud. You'll need a Weave Could service token, if you don't have a Weave token go to Weave Cloud and sign up for a Weave Cloud account.
In order to visualize the Swarm cluster with Weave Cloud you have to deploy the Weave Scope container on each Swarm node. Scope needs to run with privileged mode and because Swarm services don't support privileged mode you'll have to use a one-shot service that will provision each node with a Scope container.
$ export DOCKER_HOST=$(terraform output swarm_manager_ip)
docker run -it --rm \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
weaveworks/swarm-agents install <WEAVE-CLOUD-TOKEN>The launcher will install Scope on each server and will exit. Using --restart-condition none we
instruct Docker Swarm not to restart the service after it exits. With --mode global we make sure
Scope will be automatically deployed on new servers as you add them to the swarm.
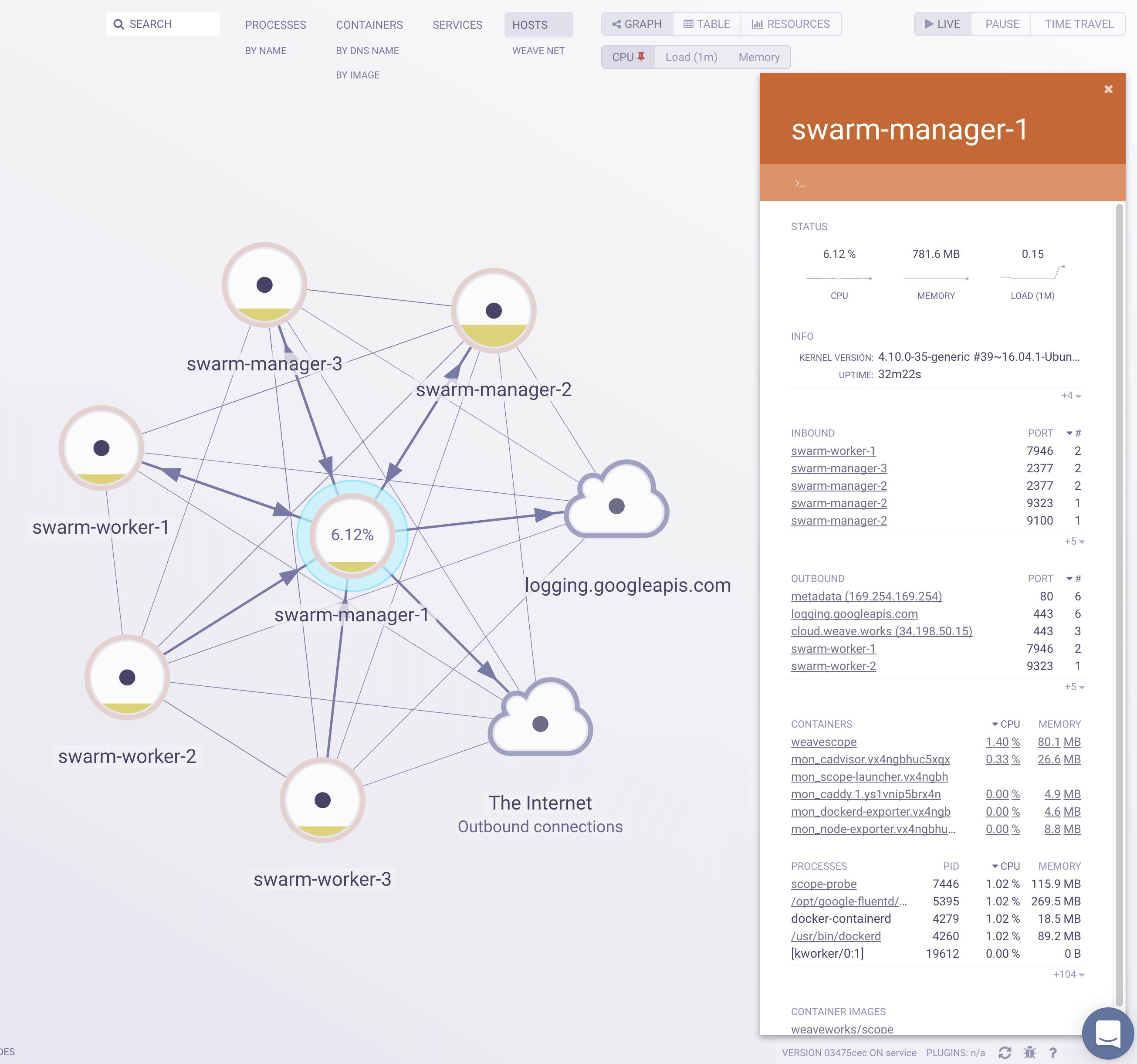
Once the Scope containers are running on all hosts you can login into Weave Cloud and inspect your cluster.
Scope offers remote access to the Swarm’s nods and containers, making it easy to diagnose issues in real-time. You can view metrics and metadata of the running processes, tasks, services, stacks and networks.
OpenFaaS setup
OpenFaaS is a framework for building serverless functions with Docker which has first class support for metrics. The GCP Cloud functions are limited to nodejs but with OpenFaaS any process can be packaged as a function. If you want to write functions in Go this is the perfect framework to do that, here is an example to get you started Serverless Golang.
Deploy OpenFaaS instrumented with Weave Cloud:
$ export DOCKER_HOST=$(terraform output swarm_manager_ip)
$ cd openfaas
WEAVE_TOKEN=<WEAVE-CLOUD-TOKEN> \
USER=admin \
PASSWORD=admin \
docker stack deploy -c docker-compose.yml faasThis will do the following:
- creates Docker configs for Prometheus, Alermanager and Caddy
- configures Prometheus with Weave Cloud remote write
- deploys Prometheus, Alermanager and the echoit function on worker nodes
- deploys the OpenFaaS gateway on a manager node
- deploys Caddy FOSS reverse proxy with basic auth for Prometheus, Alermanager and OpenFaaS Gateway
Check if OpenFaaS is working by accessing http://<SWARM-PUBLIC-IP>.
Now that you have OpenFaaS running let's do a load test to see the auto scaling in action.
You can run the load test using rakyll/hey or Apache bench.
#install hey
go get -u github.com/rakyll/hey
#do 10K requests
hey -n 10000 -c 2 -m POST -d "test" http://USER:PASSWORD@<SWARM-PUBLIC-IP>/function/faas_echoitIn the Weave Cloud UI under Explore you'll see how OpenFaaS scales up the echoit service:
Weave Cloud extends Prometheus by providing a distributed, multi-tenant, horizontally scalable version of Prometheus. It hosts the scraped Prometheus metrics for you, so that you don’t have to worry about storage or backups.
You can monitor your OpenFaaS setup by writing PromQL queries in the Weave Cloud Monitor GUI:
If you need more than what the Weave Cloud GUI offers, a Grafana Dashboard browser plugin is available that can be downloaded from the Google Chrome store.